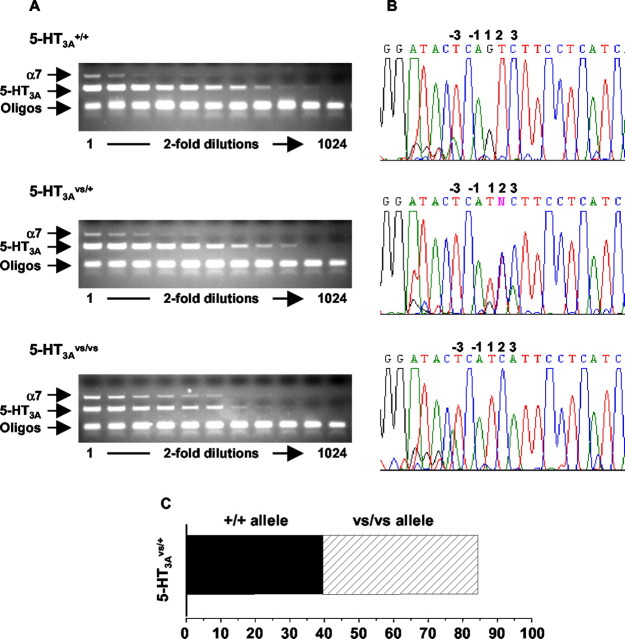
Figure 3.
RT-PCR analysis of 5-HT3A mRNA levels in mutant and wild-type mice. A, Diminished 5-HT3A mRNA levels in the 5-HT3Avs/vs mice. Total RNA was isolated from the SCG of 5-HT3A+/+, 5-HT3Avs/+, and 5-HT3Avs/vs mice as described in Materials and Methods. Serial dilutions were prepared as indicated, and 1 μl of RNA was used as template for RT-PCR analysis using primers specific for the 5-HT3A receptor (amplicon of ∼300 bp) and theα7 nACh receptor (amplicon of ∼700 bp) as an internal control. Assuming that α7 nACh receptor mRNA did not change, 5-HT3A mRNA was compared with α7 nAChR mRNA at the lowest dilution where signals could be detected. B, 5-HT3Avs/+ mice express comparable levels of the 5-HT3A mutant and wild-type mRNA. RT-PCR sequencing (B) of the products shown in A were used to estimate the relative abundance of wild-type and mutant mRNA in 5-HT3Avs/+ mice as described in Materials and Methods. The relative abundance of wild-type (solid bars) and mutant (hashed bars) sequences in the RT-PCR products from 5-HT3Avs/+ mice was determined by comparing the representation of the pure alleles, and the averaged percentage of the products is shown in the bar graph in C. Oligo, Oligonucleotide.