Figure 1.
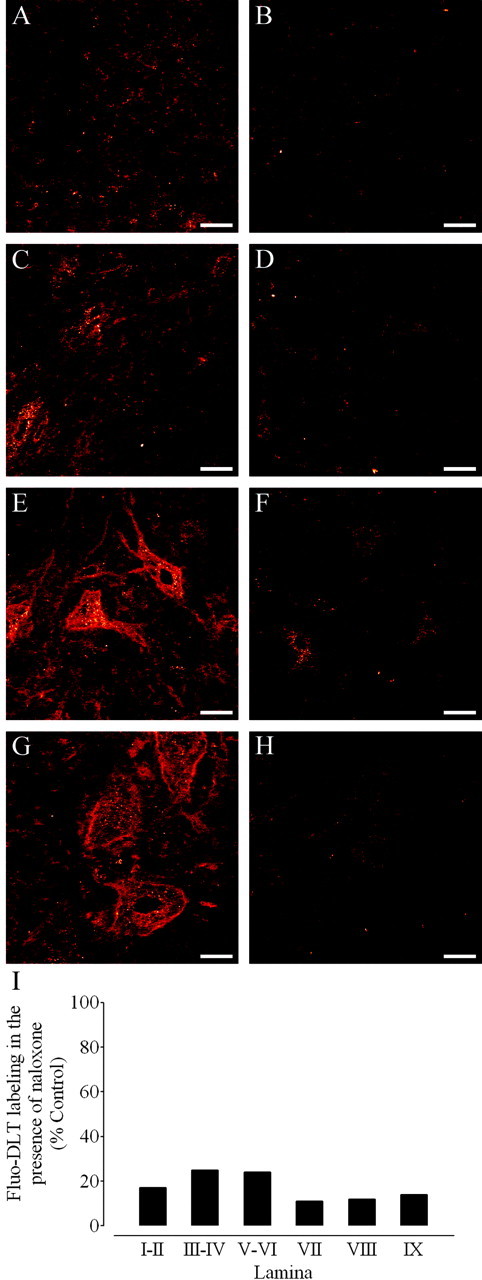
Antagonism of Fluo-DLT labeling by naloxone in the dorsal and ventral horn of the rat spinal cord. A-H, Anon-pretreated rat (control; A, C, E, G) and a rat pretreated with naloxone (B, D, F, H) were injected intrathecally with 0.8 nmol of Fluo-DLT. Internalized Fluo-DLT is observed by confocal microscopy in dorsal and ventral horn neurons of the lumbar (L4-5) spinal cord; typical images from laminas I-II (A, B), III-IV (C,D), VIII (E, F), and IX (G,H) are presented. Identical acquisition parameters were used to obtain the images for cells labeled in the presence or absence of naloxone. Images are displayed in glow-scale, where white represents the highest fluorescence intensity and red represents the lowest (black indicates the absence of fluorescent signal). Scale bar, 20 μm. I, Fluorescence labeling levels for Fluo-DLT intrathecally injected untreated (control) and naloxone-treated rats were determined as described in Materials and Methods. Each bar corresponds to the average fluorescence labeling levels of the naloxone-treated rat divided by the Fluo-DLT-labeling levels of the untreated rat calculated within each specified lamina (3 sections/animal) in one representative experiment.
