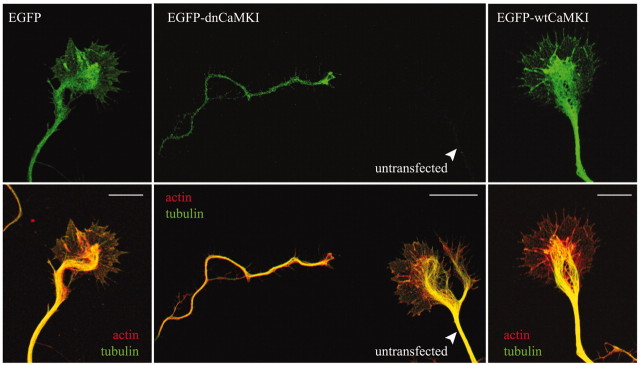
Figure 5.
Inhibition of CaMKI results in axonal growth cone collapse. Low-density hippocampal neurons were transfected with constructs encoding dn- and wtCaMKI on day 3 and then fixed 8 hr later. Cells were immunolabeled to stain tyrosinatedα-tubulin using Cy5-labeled secondary antibodies (pseudocolored green in bottom panel) and stained with tetramethylrhodamine isothiocyanate-labeled phalloidin to visualize filamentous actin (pseudocolored red in bottom panel). In neurons expressing only EGFP(left panel), the peripheral domain of the growth cone is dominated by actin(red), where as the central domain contains both actin and stabilized microtubules (green; yellow in merged image). Expression of EGFP-dnCaMKI (middle panel, top) dramatically reduced growth cone size (middle panel, left) compared with the growth cone of a neighboring untransfected neuron (middle panel, right). Both peripheral and central domains of the growth cone were essentially eliminated by expression of dnCaMKI. Expression of wtCaMKI had little effect on growth cone morphology (right panel). Scale bar, 10 μm.