Figure 2.
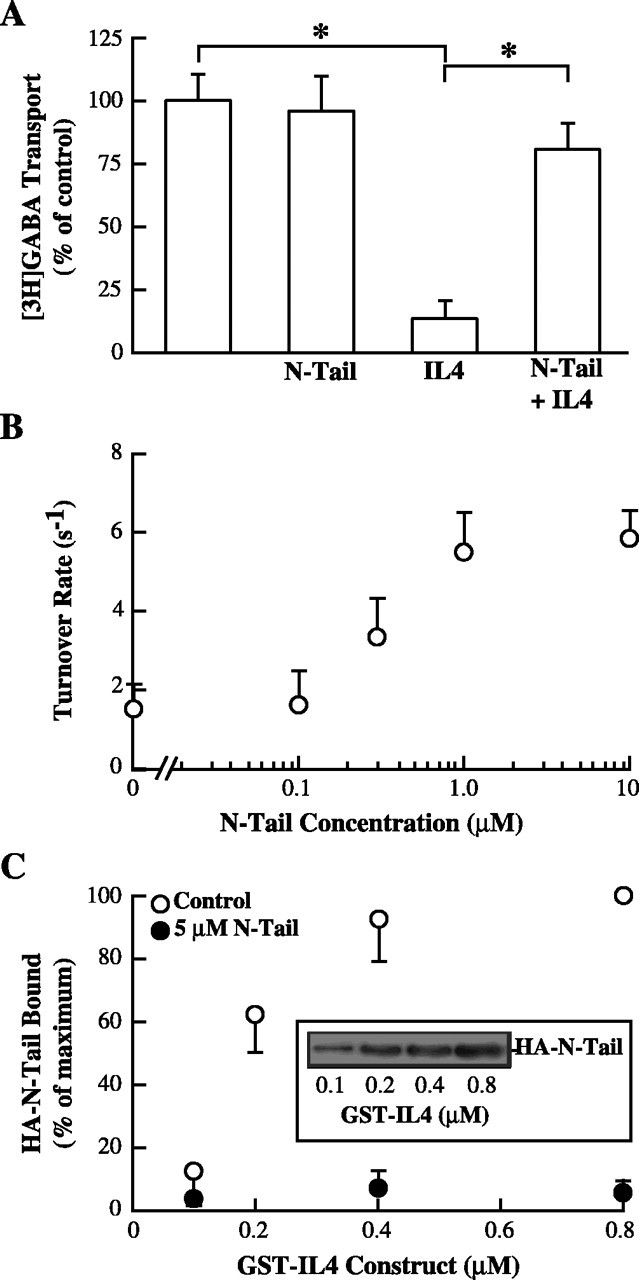
N-terminal tail and IL4 domain of GAT1 functionally interact. A, Coinjection of N-Tail peptide reverses IL4 peptide inhibition of GABA uptake. Oocytes expressing GAT1 were left untreated or injected 15 min before assay with IL4 fusion protein, N-Tail fusion protein, or both (∼1 μm) and subjected to [3H]GABA flux assays. Data are from three experiments (4-7 oocytes per condition per experiment). Asterisks indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between the two indicated groups. B, N-Tail fusion protein reverses IL4-mediated inhibition of GAT1 turnover rates. GAT1-expressing oocytes were acutely injected with 1 μm IL4 fusion protein alone or in combination with increasing concentrations of N-Tail fusion protein and then subjected to two-electrode voltage clamp. Data are from 5-11 oocytes per data point. C, N-terminal tail and IL4 domain directly interact. Recombinant GAT1 HA-N-Tail cytosolic domain was bound to increasing concentrations of GST-IL4 and immunoblotted with HA-specific Ab. Data from three experiments are plotted relative to binding with 0.8 μm GST-IL4 fusion protein in the absence (open circles) or presence (filled circles) of excess (5 μm) N-Tail fusion protein.
