Figure 4.
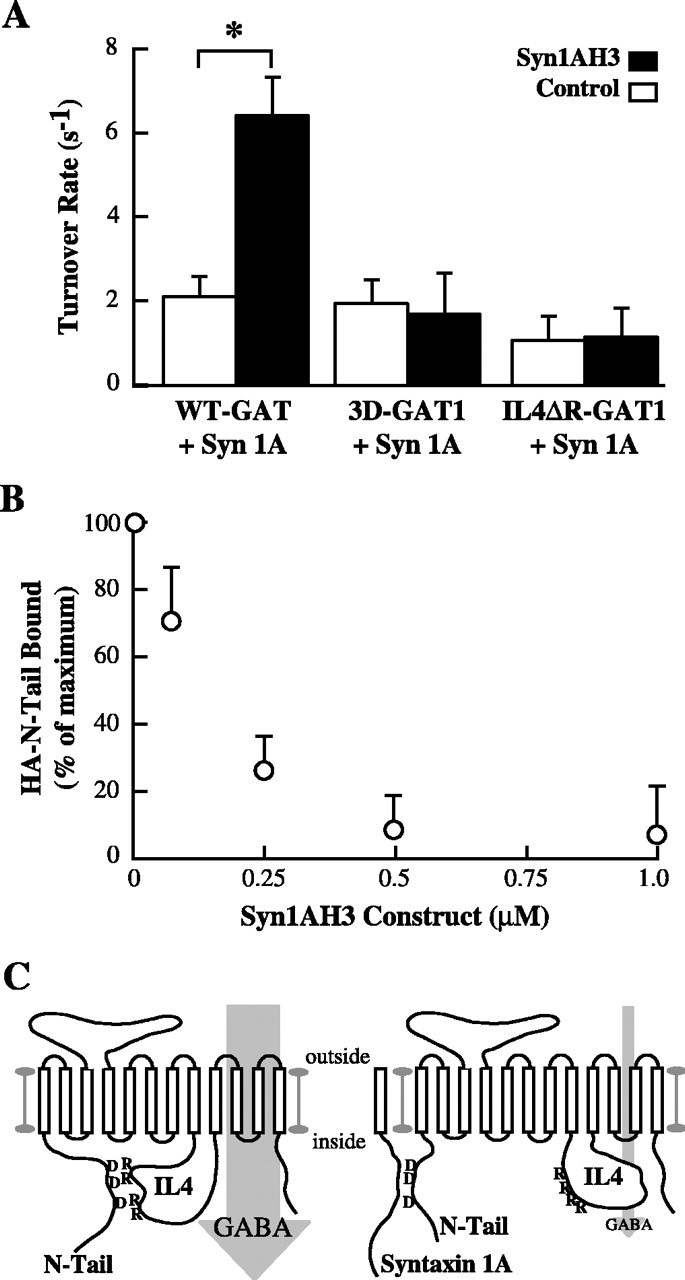
Syntaxin 1A functionally regulates the interaction between the N-terminal tail and the IL4 domain. A, Syntaxin 1A H3 domain reverses full-length syntaxin 1A inhibition of wild-type GAT1 but not N-terminal or IL4 GAT1 mutants. Oocytes coexpressing syntaxin 1A with wild-type GAT1, 3D-GAT1, or IL4ΔR-GAT1 were subjected to two-electrode voltage clamp before (open bars) and after (filled bars) acute injection with 1 μm Syn1AH3 fusion protein. Data are from 5-9 oocytes per condition. Asterisks indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between the two indicated groups. B, Syn1AH3 fusion protein inhibits the binding of the N-terminal tail to the IL4 domain. Recombinant HA-N-Tail cytosolic domain of GAT1 was bound to equal amounts of GST-IL4 domain in the presence of increasing concentrations of Syn1AH3 fusion protein and immunoblotted using HA-specific Ab. Data are from three separate experiments plotted relative to binding in the absence of Syn1AH3 fusion protein. C, A cartoon illustrating inter-domain interactions that govern GABA flux through GAT1. D, Aspartic acid residues in the N-terminal tail; R, arginine residues in the IL4 domain.
