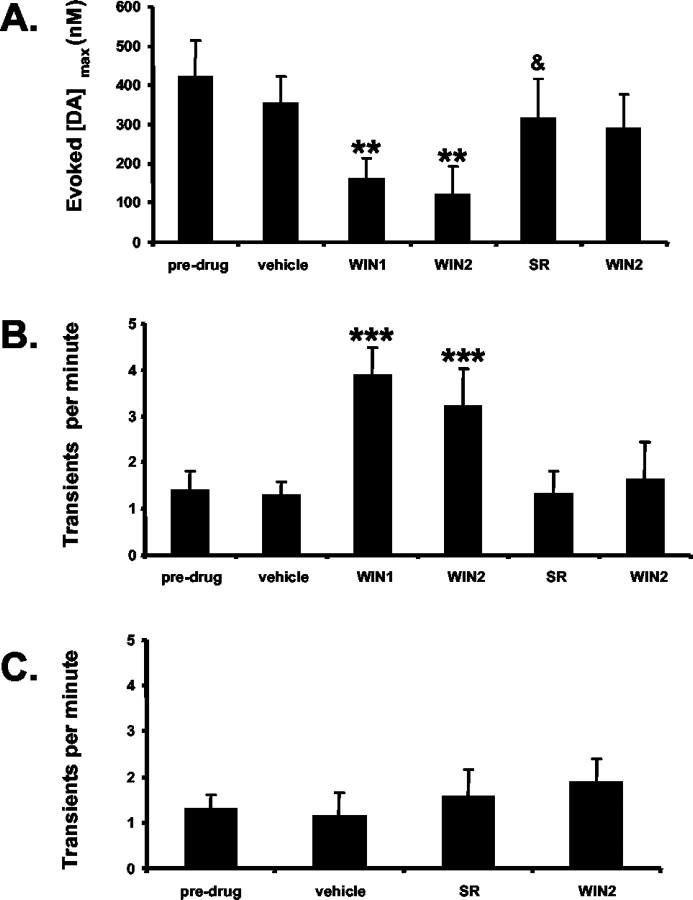
Figure 7.
Mean responses of dopamine to a cannabinoid agonist and antagonist. A, The maximal dopamine concentration ([DA]max) elicited by electrical stimulation of the MFB is decreased after the first injection of WIN (125 μg/kg; WIN1) but not further decreased by a larger dose (250 μg/kg; WIN2). This effect is reversed and prevented by SR (300 μg/kg; SR; &p < 0.05 compared with WIN2), and a subsequent injection of WIN (250 μg/kg; WIN2) does not affect this (**p < 0.005 compared with vehicle; n = 9 rats). B, The frequency of NAc dopamine concentration transients (n = 9 rats) induced by an initial injection of WIN (125 μg/kg; WIN1) and a subsequent one (250 μg/kg; WIN2). SR (300 μg/kg; SR) reversed the effects of WIN and blocked further effects of WIN (250 μg/kg; WIN2). (***p < 0.001 compared with pre-drug). C, Administration of SR (300 μg/kg; SR) does not affect the frequency of dopamine transients (n = 4 rats) but prevents changes by WIN (250 μg/kg; WIN2). In each panel, vehicle consists of a 1:1:18 ethanol/emulphor/saline (0.9%) ratio. Bolus doses were each spaced by 15 min.