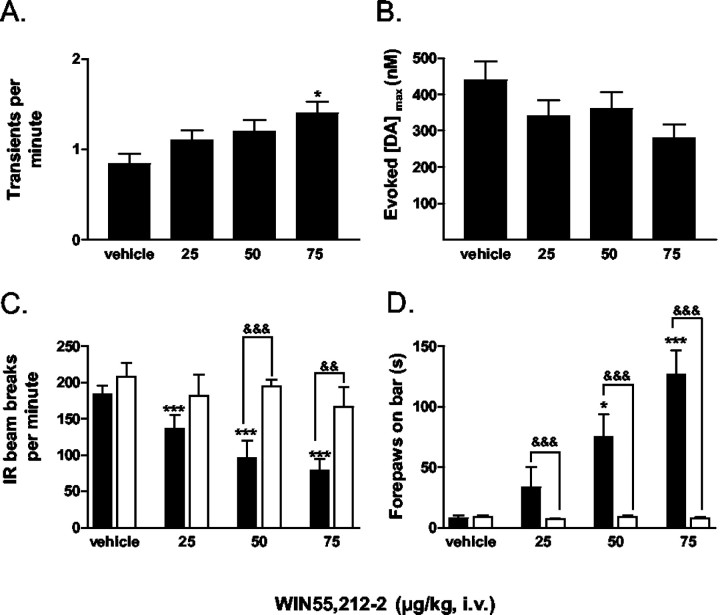
Figure 8.
Dose-dependent effects of WIN55,212–2 on dopamine release and behavior. For all panels vehicle = [1:1:18, ethanol/emulphor/saline (0.9%) ratio], 25 = 25 μg/kg, 50 = 50 μg/kg, and 75 = 75 μg/kg (n = 4 rats). Intravenous bolus doses were spaced by 15 min. A, Frequency of dopamine concentration transients in the NAc during a cumulative dosing regimen (*p < 0.05). B, The maximal dopamine concentration ([DA]max) elicited by electrical stimulation of the MFB. The response tends to decrease with the cumulative dosing regimen but was not significant at any dose. C, Locomotor activity after treatment with WIN. Black bars represent WIN-treated animals, whereas time-matched, saline controls are depicted with white bars. (***p < 0.001 compared with vehicle;&&&p < 0.001 compared with time-matched saline control;&&p < 0.005 compared with time-matched saline control). D, Administration of WIN dose-dependently increases catalepsy as measured using the bar test (*p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 compared with vehicle;&&&p < 0.001 compared with time-matched saline control).