Figure 1.
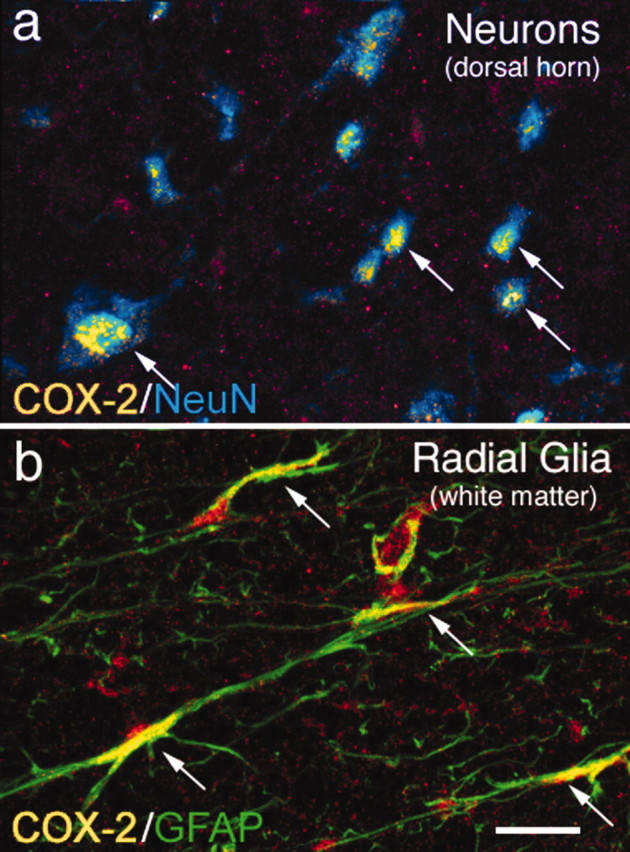
Neurons and radial glia located in the lumbar segment of the rat spinal cord constitutively express high levels of COX-2 protein. Immunohistochemical analysis reveals a high level of constitutive COX-2 expression in the majority of neurons in the rat spinal cord gray matter, as shown by colocalization of COX-2-IR (yellow) and a neuron-specific antibody, NeuN (blue; a). Confocal image analysis of 15-μm-thick sections reveals that this COX-2-IR is observed in the perinuclear region of the neuron. Radial glia in the spinal cord white matter also exhibit a high level of COX-2 expression, as shown by colocalization of COX-2-IR (yellow) and glial fibrillary acidic protein-IR (green; b) in the spinal cord white matter. Areas of colocalization appear yellow in both a and b (also indicated by arrows). Scale bar, 40 μm.
