Figure 7.
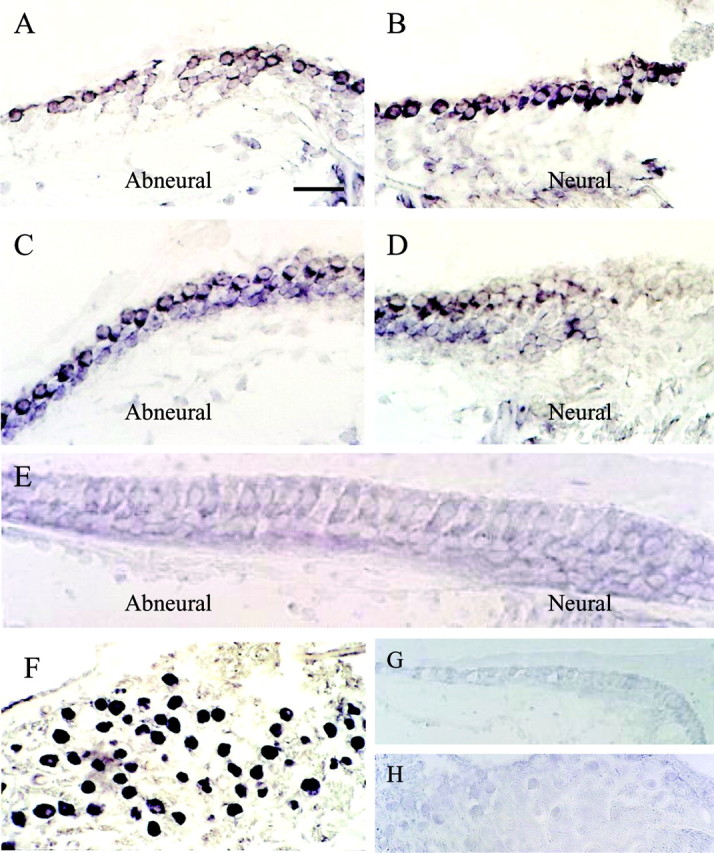
Distribution of cKv4.2 mRNA as revealed by in situ hybridization in a 2-week-old posthatched chick. A, B, Photomicrographs of the same cross section, taken from proximal regions of the chick cochlea, revealed cKv4.2 transcription in hair cells located on both abneural and neural sides when treated with antisense probe. C, In more distal regions of the same epithelium, where there is a gradation from short to tall hair cells across the width of the epithelium, cKv4.2 was transcribed only in hair cells located on the abneural side. D, Tall hair cells from the same section as in C showed no signal. These cells are positioned slightly tangential. E, Hair cells in the distal-most part of the sensory epithelium are tall, and cKv4.2 mRNA was absent from these cells. F, Additionally, cKv4.2 mRNA was found in the soma of the cochlear ganglion cells. G, H, In comparison, sections treated with cKv4.2 sense probe showed an absence of signal in both the sensory epithelium (G) and ganglion cells (H). Sections of cochlea shown are ∼1700 μm (A, B), 500μm (C, D), 120 μm (E), 1700 μm (F), and 1500 μm (G, H) from the distal tip of the epithelium. Scale bar: (in A) A-D, 25 μm; E, 18 μm; F, 45 μm; G, 30 μm; H, 50 μm.
