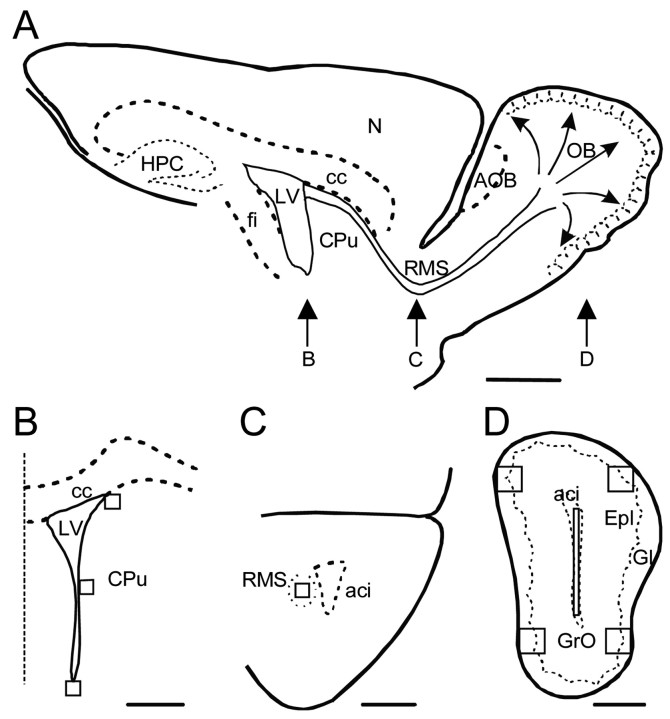
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the analyzed regions. A, Drawing of a sagittal section of the mouse brain, indicating the anatomical location of the coronal sections in B-D. Neural precursors in the lateral wall of the lateral ventricle (LV) migrate tangentially through the RMS to the OB and then migrate radially and differentiate in the granular and glomerular cell layers. B, Drawing of a coronal section through the subventricular zone showing the position of the areas (125 × 125 μm) in which BrdU+ cells were counted. The dotted line represents the midline. C, Drawing of a coronal section showing the position of the square (same size as in B) used to quantify the number of cells that recently underwent mitosis in the RMS. D, Coronal view of the OB, in which four areas (250 × 250 μm), including the granule cell (GrO) and the glomerular (Gl) layers, were analyzed. In some experiments, the number of BrdU+ cells was also counted in a rectangular area (25 × 1000 μm) in the central part of the OB, where tangentially migrating cells from the SVZ enter the OB before starting their radial migration. aci, Anterior commissure; AOB, accessory olfactory bulb; cc, corpus callosum; CPu, caudate-putamen; Epl, external plexiform layer; fi, fimbria hippocampi; HPC, hippocampus; N, neocortex. Scale bars: A, 1 mm; B-D, 500 μm.