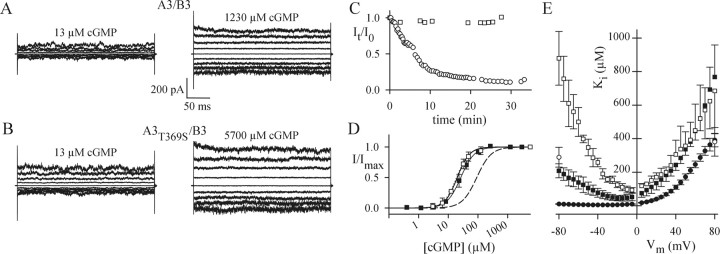
Figure 6.
Electrophysiological properties of heteromeric channels. A, Current recordings of A3/B3 channels in inside-out patches. A3/B3 channels were activated with 13 or 1230 μm cGMP. The voltage protocol was as in Figure 4A. B, Current recordings of A3T369S/B3 channels in inside-out patches. A3T369S/B3 channels were activated with 13 or 5700 μm cGMP. The voltage protocol was as in Figure 4A. C, A progressive decline of maximal cGMP-activated currents of homomeric A3T369S (open circles) is not observed with heteromeric A3T369S/B3 channels (open squares). Data points represent current amplitudes measured at +80 mV and normalized to the amplitude of the first recording at t = 0. D, Ligand sensitivity of heteromeric channels. Normalized currents (I/Imax) at -80 mV versus cGMP concentration for A3/B3 (filled squares) and A3T369S/B3 (open squares) are shown. Symbols represent mean values ± SD. Error bars were omitted for N = 2 recordings. Solid lines were calculated with the Hill equation with the following parameters: K1/2, 26.3 ± 5.9 μm; n = 1.9 ± 0.1 (A3/B3; N = 4); and K1/2, 20.1 ± 1.5 μm; N = 2.1 ± 0.6 (A3T369S/B3; N = 3). For comparison, the dose-response relations for A3 (dotted line) and A3T369S (dashed line) are included. E, Voltage dependence of Ca2+ blockage. Mean Ki values of Ca2+ blockage versus voltage for homomeric A3 (filled circles; N = 6), A3T369S (open circles; N = 5), heteromeric A3/B3 (filled squares; N = 3), and A3T369S/B3 (open squares; N = 3) channels are shown. Ki values for A3T369S were obtained for -80 and +80 mV only. Error bars indicate SD.