Figure 1.
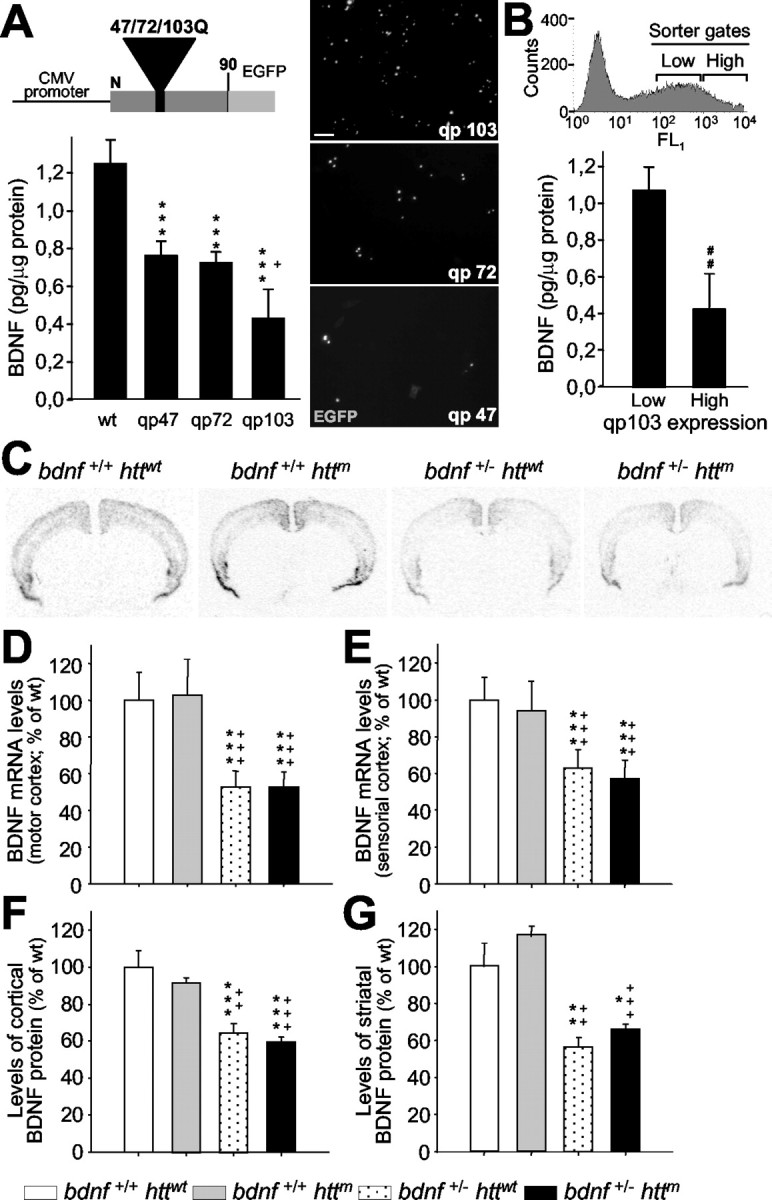
The number of CAG repeats and the levels of mutant htt expression modulate the expression of BDNF. A, ELISA for BDNF was performed on the culture media from wt M213 cells and subclones expressing exon 1 of mutant htt with 47 (qp47), 72 (qp72), and 103 CAG/CAA repeats (qp103). The expression of this neurotrophin decreases as the number of repeats is longer. The scheme at the top shows the structure of qp constructs, which expresses a fusion protein of the first 90 amino acids of the mutant htt and the EGFP. The right panels are photomicrographs of transfected cells with the qp47, 72, and 103 constructs, which show the mutant htt inclusions. CMV, Cytomegalovirus. Scale bar, 50 μm. B, Transfected cells that express different levels of qp103 were collected by cell sorting (inset shows sorting gates), and BDNF levels were assessed. The amount of BDNF in culture media is inversely proportional to the levels of expression of qp103. ***p<0.001 compared with wt cells; +p<0.05 compared with qp47 or qp72; ##p < 0.005 compared with low levels of qp103 expression. C-G, BDNF levels are not affected by the mutant exon 1 of Htt in R6/1 (bdnf+/+ httm). C-E, In situ hybridization demonstrates that mutant htt does not change the levels of bdnf expression either in the motor cortex (D) or in the sensorial cortex (E). C, A Representative coronal section (bregma, +1.1 mm) of bdnf in situ hybridization of the four genotypes analyzed. F, G, In addition, the levels of BDNF protein detected by ELISA are not modified by mutant htt in the cortex (F) or in the striatum (G). The only changes in mRNA or protein are detected in bdnf+/- mice with or without mutant htt (C-G). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, and ***p < 0.001 compared with wt mice (bdnf+/+ httwt); ++p < 0.005 and +++p < 0.001 compared with R6/1 mice (bdnf+/+ httm).
