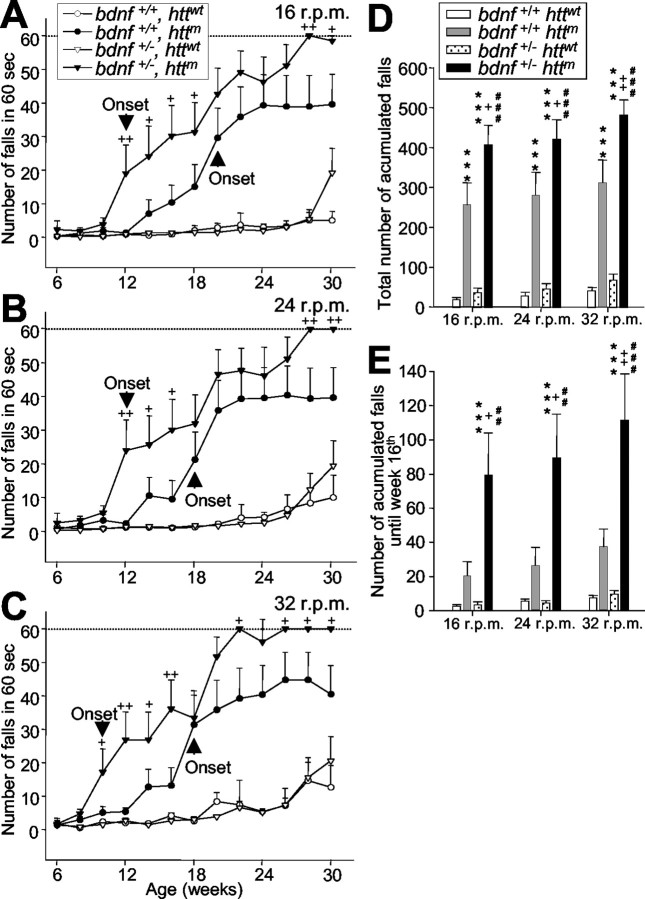
Figure 3.
Lower BDNF levels cause earlier onset and more severe motor dysfunctions in mutant htt mice. A-C, bDM (bdnf+/- httm) show more deficits on the rotarod than R6/1 mice (bdnf+/+ httm) tested at 16 rpm (A), 24 rpm (B), or 32 rpm (C) (p < 0.001; F-Wald test). +p < 0.05 and ++p < 0.005 compared with R6/1 mice (bdnf+/+ httm). bDM show earlier symptoms at all revolutions assayed, and the onset of motor deficits (expressed as the first significant time point with respect to control animals; A-C, arrowhead) showed advances from 6-8 weeks with respect to R6/1 mice (bdnf+/+ httm; A-C). D, In addition, bDM show more severe symptoms. The total number of accumulated falls in the period examined is significantly different between mutant htt mice with normal or low levels of BDNF. E, During early stages, the differences in the severity of motor deficits (measured as the total number of falls up to the age of 16 weeks) between R6/1 mice and bDM are very large. D, E, ***p < 0.001 compared with wt mice (bdnf+/+ httwt); +p < 0.05 and ++p < 0.005 compared with R6/1 mice (bdnf+/+ httm); ##p < 0.005 and ###p < 0.001 compared with bdnf heterozygous mice (bdnf+/ - httwt).