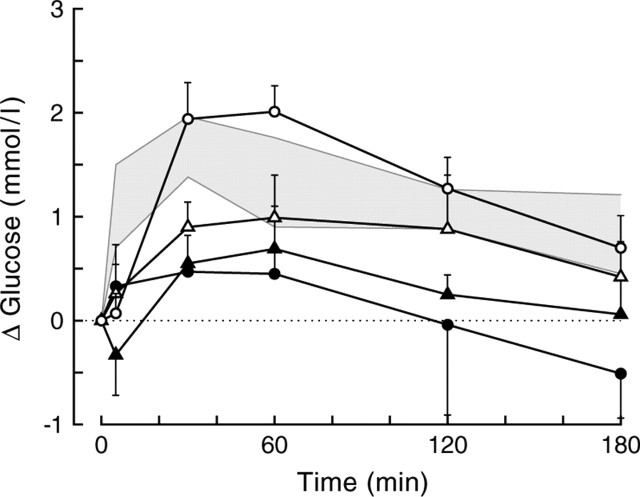
Figure 8.
Plasma glucose changes during BIC administration into or outside the PVN of liver-intact animals. Five different treatment groups are displayed. The gray shading indicates the mean ± SEM from the original group of PVN infusions (group A). Probe placements for the additional control group are divided in those within or touching the PVN (group B; open circles; n = 7), those within <1 mm of the caudal borders of the PVN (group C1; open triangles; n = 7), those within <1 mm of the lateral or rostral borders of the PVN (group C2; closed triangles; n = 5), and those > 1 mm away from the caudal border of the PVN (group D; closed circles; n = 5). Depending on whether groups C1 and C2 were separated or combined, the MANOVA for the overall data showed significant effects of group (p = 0.023 and p = 0.019, respectively) and group × time (p = 0.092 and p = 0.018, respectively). Comparing the different groups displaying probe placements outside the PVN (i.e., C1, C2, D) with the within-PVN placement group (i.e., B) revealed significant group effects for groups C2 and D (p = 0.003 and p = 0.008, respectively) and significant group × time effects for groups C1, C2, and D (p = 0.035, p = 0.024, and p = 0.052, respectively). When compared with the original within-PVN group (i.e., the gray area), significant effects of group were found for groups C and D (p = 0.033 and p = 0.007, respectively), and a significant group × time effect was found for group B (p = 0.045). Separating group C in caudal (C1) and lateral plus rostral (C2) placements revealed that only group C2 differed significantly from group A (p = 0.004 for the effect of group). In all groups except for groups C2 and D, the within-animal comparison showed significant effects of day and day × time (i.e., the BIC day differs significantly from the control day).