Figure 1.
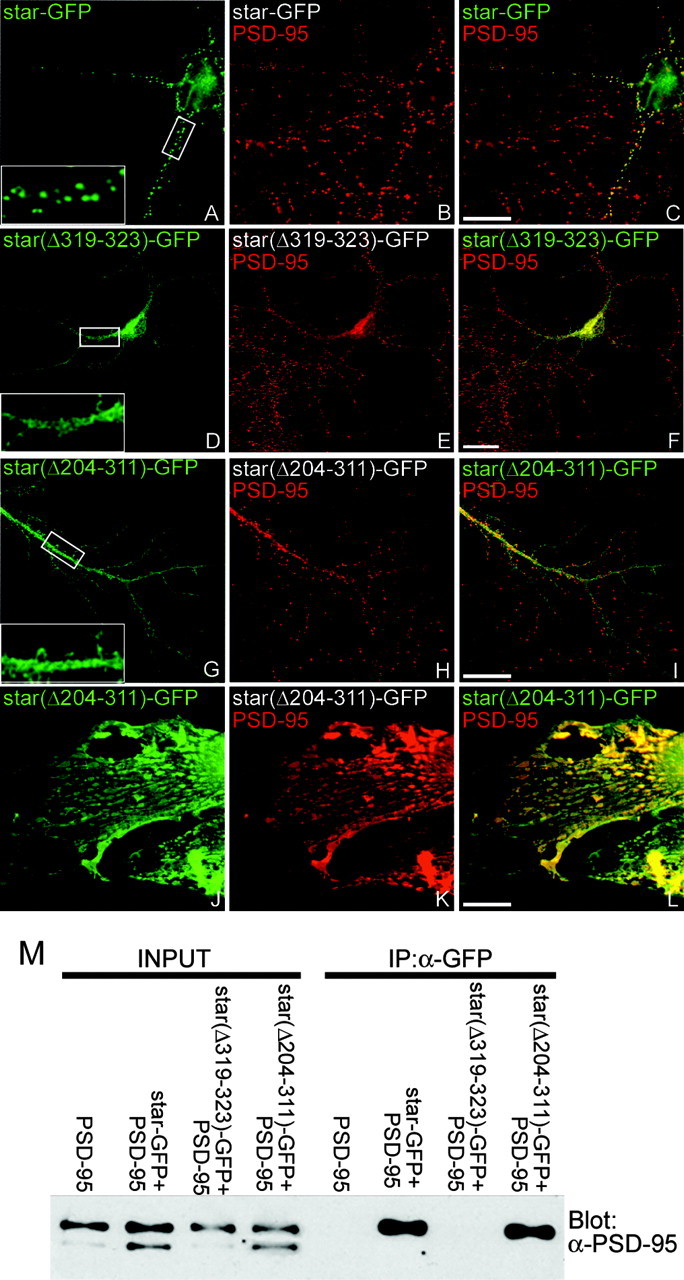
The stargazin PDZ ligand and C terminus are both necessary for stargazin synaptic targeting. Constructs encoding stargazin-GFP (star-GFP), stargazin(Δ319-323)-GFP [star(Δ319-323)-GFP], or stargazin(Δ204-311)-GFP [star(Δ204-311)-GFP] were transfected into neurons (A-I), which were then fixed (at 11-17 d in vitro) and stained for GFP (green) and PSD-95 (red). A-C, Stargazin-GFP clusters at synaptic sites. Stargazin lacking the PDZ-binding domain, stargazin(Δ319-323)-GFP, does not target to synapses (D-F). Similar to the construct lacking the PDZ-binding domain, a construct lacking all of the intracellular C-terminal tail, except the last 11 amino acids, stargazin(Δ204-311)-GFP was also diffusely localized in neurons (G-I). In contrast, when cotransfected with PSD-95 in COS-7 cells, stargazin(Δ204-311)-GFP was clustered by PSD-95 (J-L). Merged images are shown in C, F, I, and L. The insets in A, D, and G are digitally magnified 3.5×. Scale bar, 10 μm. M, COS-7 cells were transfected alone or with the indicated combinations of PSD-95, stargazin-GFP (star-GFP), stargazin(Δ319-323)-GFP [star(Δ319-323)-GFP], or stargazin(Δ204-311)-GFP [star(Δ204-311)-GFP]; cell lysates were prepared, and GFP was immunoprecipitated (IP). Although PSD-95 interacted strongly with stargazin-GFP and stargazin(Δ204-311)-GFP, stargazin(Δ319-323)-GFP failed to coimmunoprecipitate. Input corresponds to 5% of total lysate.
