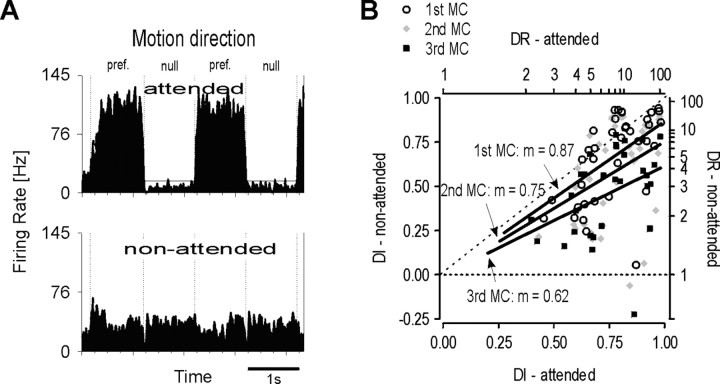
Figure 4.
Near-bar experiment. Conventions are the same as in Figure 2. A, For the attended condition (top histogram), this single unit showed strong direction selective responses, but with attention directed away from the RF (bottom histogram), direction selectivity disappeared. Note that this is caused not only by a decrease of responses to preferred motion but by a multifold increase of responses to nonpreferred motion. See Results for details. B, Attention-dependent modulation of direction selectivity in the population of MT neurons during the first three motion cycles (MCs). Straight lines fitted to the data points of each MC indicate strongly decreasing direction selectivity when attention is withdrawn from the RF with the highest reduction of ∼40% during the third cycle.