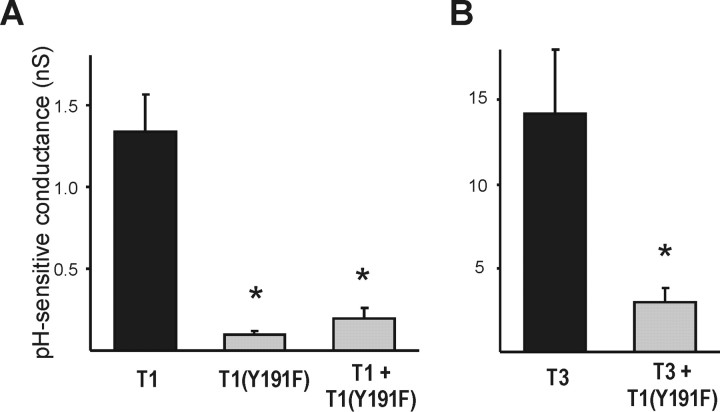
Figure 2.
A TASK-1 construct bearing a point mutation in the second pore domain (Y191F) acts as a dominant negative of TASK-1 (T1) and TASK-3 (T3) channels. HEK 293 cells were transfected with the indicated constructs and recorded under whole-cell voltage clamp by using a ramp voltage protocol (-130 to 20 mV; 0.2 V/sec). Whole-cell conductance was calculated as the slope of the current evoked between -130 and - 60 mV, and the pH-sensitive conductance was determined as the difference in conductance at pH 8.4 and 5.9. A, Expression of TASK-1(Y191F) by itself generated no pH-sensitive conductance, and coexpression of TASK-1(Y191F) abolished the pH-sensitive conductance generated by wild-type TASK-1 (left; from 1.3 ± 0.2 to 0.1 ± 0.02 nS; *p < 0.05, ANOVA). A total of 6 μg of DNA was transfected in all cases, with TASK channel constructs transfected at 3 μg each and the balance provided by empty pcDNA3 vector. B, Importantly, TASK-1(Y191F) also eliminated pH-sensitive conductance from coexpressed TASK-3 channels (right; from 14.2 ± 3.8 to 3.0 ± 0.8 nS; *p < 0.05, t test). A total of 9 μg of DNA was transfected in each experiment, with GFP-TASK-3 at 2 μg and either TASK-1(Y191F) or pcDNA3 at 7 μg.