Figure 4.
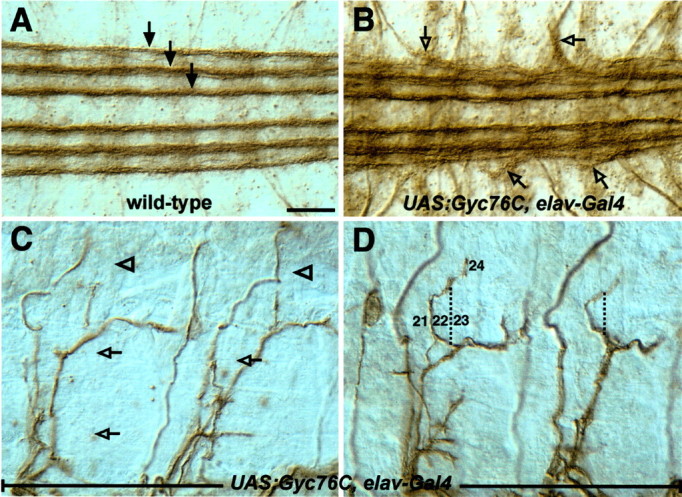
Neuronal overexpression of Gyc76C perturbs CNS and motor axon guidance. Shown are filleted preparations of late stage 16 embryos stained with the anti-fasciclin II monoclonal antibody 1D4 to reveal a subset of CNS axons (A, B) and motor axons (C, D). Anterior is left, and dorsal is up. A, In a wild-type embryo, three well separated bundles of axons are present on each side of the CNS midline (arrows). B, Overexpression of Gyc76C in all neurons with the Gal4-UAS system in a wild-type background results in the third/outermost longitudinal axon fascicle defasciculating abnormally and projecting axons away from the CNS (open arrows). C, Overexpressing Gyc76C in all neurons produces motor axon guidance defects in which axons often fail to defasciculate from the ISNb and SNa axon bundles. D, Overexpressing Gyc76C in all neurons also results in a novel phenotype affecting the dorsal branch of the SNa, which now projects incorrectly between muscles 21 and 22 and then extends toward its proper target, muscle 24. The path that this bundle of SNa axons normally follows is indicated by the dashed line. Scale bar: A-D, 10 μm.
