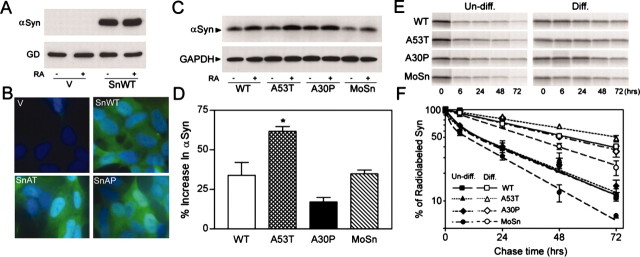
Figure 4.
Neuronal differentiation and A53T mutation lead to increased stability of α-Syn proteins. A, B, Characterization of polyclonal SH-SY5Y cells expressing Huα-Syn. A, Immunoblot analysis of extracts from vector-transfected control (V) and WT Hα-Syn (SnWT) cell lines shows that very little, if any, endogenousα-Syn can be documented in both naive and RA-treated cells. The α-Syn bands are near saturation because the protein loading (5 μg) was twice that used for quantitative analysis of α-Syn protein. GAPDH (GD) is shown as the reference protein. B, Immunofluorescence analysis of Huα-Syn expression in the SH-SY5Y cell lines. Greater than 95% of the Huα-Syn cell lines showα-Syn expression (green), whereas very few cells show Huα-Syn expression in the vector-transfected cell line. The cells were counterstained with DAPI (blue). C, Polyclonal SH-SY5Y cell lines, stably expressing Huα-Syn variants (WT, A53T, A30P) and Moα-Syn (MoSn), were differentiated by RA treatment. The immunoblot analysis of α-Syn expression in undifferentiated (-) and RA-differentiated (+) SH-SY5Y cells shows that differentiation is associated with increased accumulation of α-Syn polypeptide. Parallel immunoblot analysis for GAPDH (GD) confirms equal protein loading. D, The immunoblots shown in C were subject to quantitative analysis, and the percentage increase of totalα-Syn levels associated with RA differentiation was plotted. Although all Huα-Syn variants and Moα-Syn levels increase with differentiation (p < 0.01; t test), the increase in the level of A53T mutant Huα-Syn is significantly higher (*p < 0.05; t test) than other α-Syn variants. Each value represents mean and SEM from three independent cultures. E, F, Undifferentiated and RA-differentiated polyclonal SH-SY5Y cells expressing α-Syn were subjected to pulse-chase analysis to determine the stability of α-Syn variants. E, Representative autoradiograms showing [35S]methionine-labeled, immunoprecipitated α-Syn at various times (0, 6, 24, 48, and 72 hr) after metabolic labeling of SH-SY5Y cells. F, The stability of newly synthesizedα-Syn increases with neuronal differentiation. The levels of [35S]methionine-labeled α-Syn were quantified, and the percentage changes, relative to the 0 hr point, are plotted (n = 3; SEM). Note that differentiation is associated with increased stability of all α-Syn variants. Although the rates of decay for all three Huα-Syn variants are similar with the undifferentiated cells, A53T mutant Huα-Syn exhibits slower decay in differentiated cells. Consistent with the lower steady-state levels of accumulation, Moα-Syn is metabolized by the cells faster than Huα-Syn.