Table 1.
Principal definitions, symbols, and default parameter values used in equations
|
Symbol |
Identification |
Definition/values used |
|---|---|---|
| N | Number of neurons in network | 3000 (24,000 in some network simulations) |
| k | Number of synapses per neuron | 30 (for CA1), 90 (for CA3) |
| s | Spontaneous firing rate of a single neuron per time step of size τd | 0.0315 × τd |
| τR | Absolute refractory time of neuron | 28 msec (IF), 36 msec (Poiss, HH) |
| τd | Synaptic time delay | 2.8 msec (IF), 3.7 msec (Poiss), 1-5 msec (HH) |
| ρ | Proportion of long-distance connections generated by breaking a synapse and rewiring it to a randomly chosen postsynaptic cell | Varied from 1.0 × 10−5 to 0.4 |
| p1 | Synaptic strength (i.e., probability that postsynaptic neuron will fire given that a particular presynaptic neuron fired) | 0.025 |
| p2 | Probability that two postsynaptic neurons fire given the presynaptic neuron fired (dependent on k and p1) | p2 = 1 - (1 - p1)k - kp1(1 - p1)k−1 |
| α | Approximate number of neurons in wave front | k/2 - 1 |
| R | Number of time steps that a neuron remains refractory | R = τR/τd ≈ 10 |
| Wi | Number of waves present in network at time i | Wi + 1 = f(Wi) |
| ei | Number of excitable neurons in the network at time i |
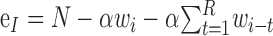 or ei = N − αwi(1+R) (for one-dimensional map) or ei = N − αwi(1+R) (for one-dimensional map) |
| ni | Number of new waves generated at time i resulting from long-distance connections | ni = (2αWi kρ)(p1p2ei/N) + Si |
| di | Number of waves that die in time step i resulting from wave collision | di = 2αWi/ei |
| Si | Spontaneous wave generation resulting from spontaneous cellular activity | Si = seip2 |
| W* | Number of waves in network where new wave rate and dying wave rate are equal (equilibrium point) | f(W*) = W* |
|
f(Wi) |
Function describing number of waves on next time step given number of waves on time step i
|
f(Wi) = Wi + ni − di
|
