Figure 5.
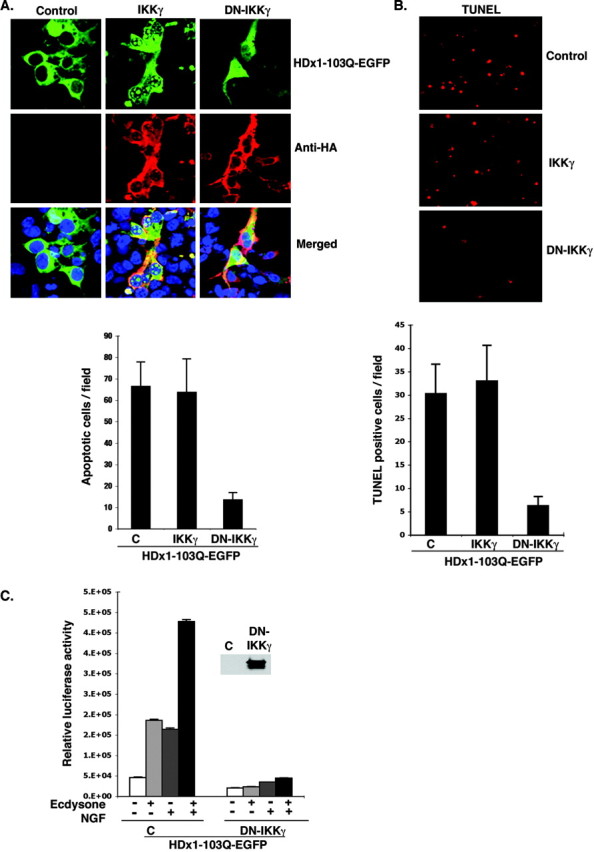
DN-IKKγ reduces the toxicity of mutant HDx1. A, IKKγ promotes aggregation and nuclear localization of Htt. HEK-293 cells were transfected with mutant HDx1-EGFP plus the indicated IKK constructs using lipofectamine and incubated for 16 hr. Cells were fixed and stained for IKKγ with anti-HA antibody (red), and cell nuclei were stained with Toto-3. Slides were examined with a confocal microscope. Conditions were such that mutant HDx1 did not cause aggregation on its own. The graph shows the average number of apoptotic bodies per microscopic field for each sample evaluated 2 d after transfection. Data are average counts of apoptotic cells from three experiments and six random microscope fields for each sample. B, DN-IKKγ expression reduces the toxicity of mutant HDx1. HEK-293 cells were transfected as in A for 16 hr. Apoptotic cells were identified by TUNEL assay as described in Materials and Methods. The top panel shows representative microscopic fields with TUNEL+ cells in each sample. The graph shows the average number of TUNEL+ cells in 16 microscopic fields from three experiments. C, DN-IKKγ blocks HDx1-induced NF-κB activation. Mutant HDx1 cells were cotransfected with NF-κB reporter and HA-tagged DN-IKKγ and β-gal plasmids and processed as described in Figure 1 A. Transfections were normalized to β-gal units from control, noninduced HDx1. Results are shown as relative luciferase units and are representative of at least three independent experiments. Data points are the average of triplicate measurements. Expression of DN-IKKγ was confirmed by Western blotting using an anti-HA antibody (inset).
