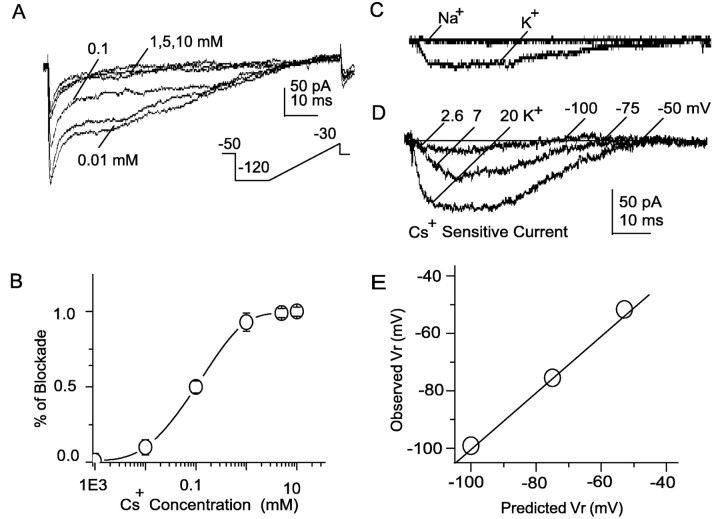
Figure 2.
Characterization of IRKC. A, Extracellular application of Cs+ blocked IRKC in a concentration-dependent manner. B, The concentration–response curve for Cs+ blockade of IRKC (IC50 of 0.12 mm; n = 4 for each data point). C, The IRK channels selectively conduct K+ ions. When K+ was replaced with Na+ in the bath, no Cs+-sensitive IRKC was observed. D, The ionic selectivity of IRKC was examined by testing the reversal potential (Vr). The Vr was –50 mV when the concentration of extra cellular K+ was 20 mm (n = 7). Vr changed to –75 and –100 mV when the concentration of K+ in the bath was shifted to 7 mm (n = 4) and 2.6 mm (n = 4), respectively. E, The Vr could be theoretically predicted with the Nernst equation. The observed Vr was consistent with the predicted value, indicating the high K+ selectivity of IRK channels. The slope of the line is 1.