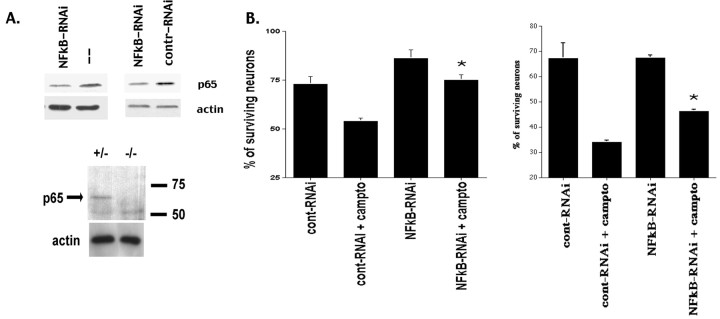
Figure 8.
NF-κB p65 suppression by RNA interference (RNAi) protects cortical neurons against camptothecin-induced neurotoxicity. Cortical neurons were transfected with short-interfering RNA (siRNA) oligonucleotides as described in Materials and Methods. A, Top, The levels of p65 protein were reduced in neurons that had been transfected with p65 RNAi (NF-κB-RNAi) as compared with nontransfected cells (–) or cells that had been transfected with nonspecific scrambled RNAi (contr-RNAi; 48 hr after transfection). β-Actin blot was provided as a loading control. Similar results were obtained by using both transfection strategies as described in Materials and Methods. A, Bottom, The specificity of the p65 antibody is demonstrated by using cortical cultures obtained from p65-deficient and wild-type littermate controls. B, Survival of cortical neurons, transfected with p65 NF-κB or control nonspecific RNAi and treated with camptothecin or vehicle for 12 hr, was assessed by nuclear morphology. Two independent experiments with different transfection methods are shown. Right, GeneSilencer; left, Lipofectamine 2000 (see Materials and Methods). Each data point is the mean ± SEM of three separate cultures. *p < 0.05 (t test) when comparing cont-RNAi + campto versus NF-κB-RNAi + campto.