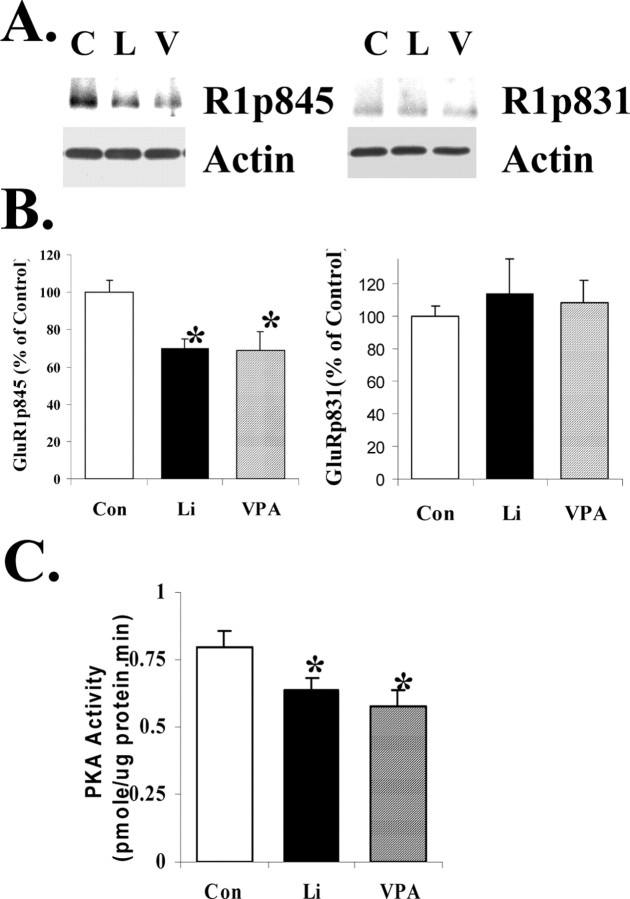
Figure 9.
Both GluR1 phosphorylation at the PKA site and PKA autonomous activity were reduced in lithium- and valproate-treated animals in hippocampus. A, B, Phosphorylation of GluR1 in hippocampus from lithium (L) or valproate (V) chronically treated animals. C, Control. Rats were treated with lithium or valproate for 4 weeks; hippocampal tissues were isolated and homogenated. Equal amounts of homogenate proteins were separated by gel electrophoresis and analyzed with anti-GluR1p845, anti-GluR1p831, and anti-actin antibodies. The bands were analyzed by the Kodak Imaging System (n = 8 for all three groups; ANOVA; *p < 0.05). C, PKA activity in hippocampus from lithium or valproate chronically treated animals. Protein samples were prepared from one hippocampus of lithium- or valproate-treated animals. Equal amounts of proteins were assayed for PKA activity (n = 8 for all three groups; ANOVA; *p < 0.05).