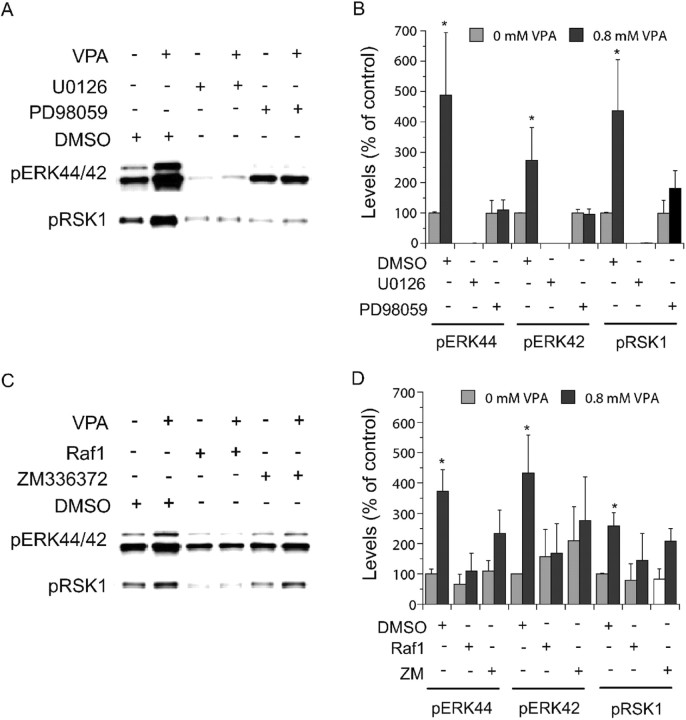
Figure 4.
Involvement of ERK pathway components in valproate-(VPA) induced ERK pathway activation. E18, DIV 8 cortical cells obtained as described in Figures 2 and 3 were treated with valproate (0.8 mm) in the absence or presence of indicated inhibitors for 2 d. Immunoblotting was conducted as described in Figures 2 and 3. MEK inhibitors [PD98059 (50 μm) and U0126 (10 μm)] (A, B) and Raf inhibitors [Raf inhibitor I (1 μm) and ZM336372 (10 μm)] (C, D) attenuated valproate-induced increases in phospho-ERK44/42 and phospho-RSK1. U0126 and Raf1 inhibitor I attenuated basal phospho-ERK44/42 and phospho-RSK1 (A-D). Bar graphs (B, D) depict densitometric results representing mean ± SE from three or more sets of samples immunoblotted in duplicates on two gels as presented in A and C. *p < 0.05 compared with cells treated with DMSO alone.