Figure 1.
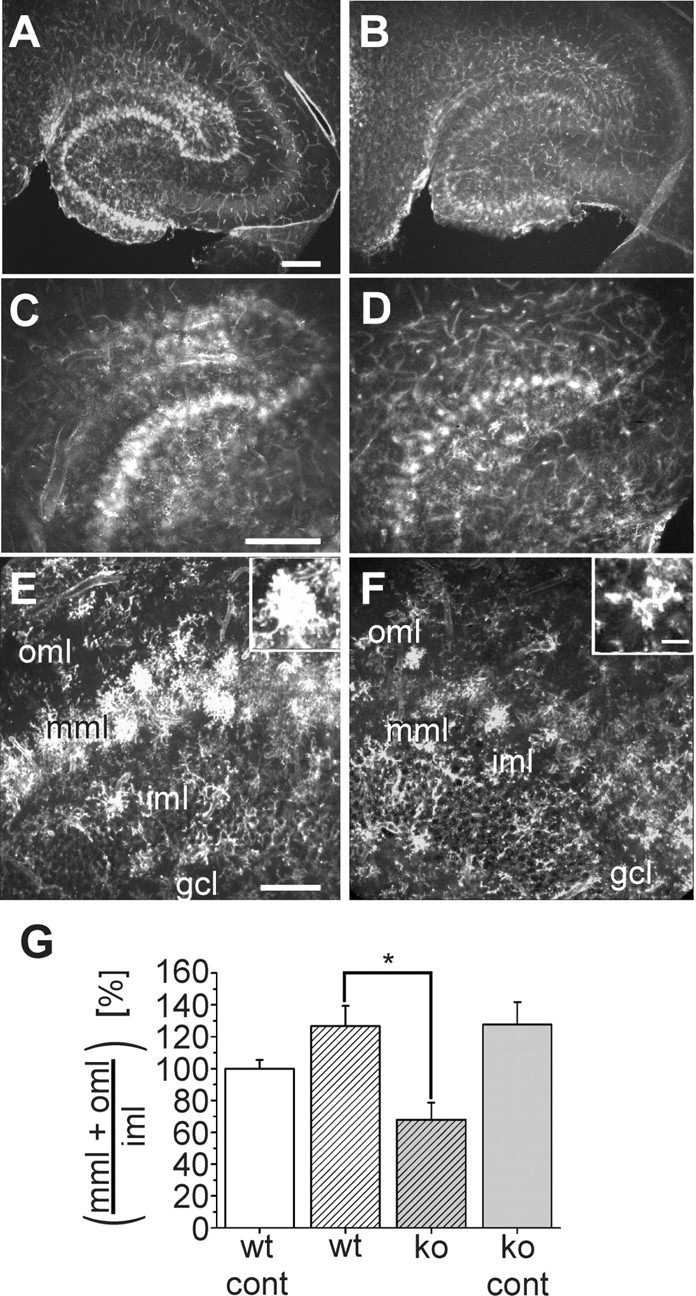
Distribution and morphology of Alexa Fluor 594-coupled lectin-positive microglia in the hippocampus of wild-type and CXCR3 knock-out mice 3 d after entorhinal cortex lesion. A-F, Horizontal vibratome sections of the temporal hippocampal formation were stained with Alexa Fluor 594-coupled lectin 3 d after entorhinal cortex lesion. A, B, Overviews of the lesioned hippocampus of wild-type animals (A) and CXCR3 knock-out animals (B). C, D, Magnified areas from A, B, respectively. E, F, Areas from the dentate granule cell layer (gcl), inner molecular layer (iml), middle molecular layer (mml), and outer molecular layer (oml) in more detail. In wild-type animals, lectin-stained microglial cells are visible in the oml and mml. In CXCR3 knock-out animals, microglial cells are restricted to the mml. Note the different morphologies of the microglial cells in CXCR3 knock-out and wild-type animals, as shown in the insets. Scale bars: A-D, 250 μm; E, F, 100 μm. G, Analysis of the number of microglial cells in slices from three wild-type and knock-out mice on the contralateral (cont) and lesioned sides. The number of microglia in CXCR3 knock-out (ko) animals on both sides and in wild-type (wt) animals on the lesioned side was normalized to the number of microglia in the wild-type animals on the contralateral side and presented as percentage of wild type ± SEM. *p < 0.05.
