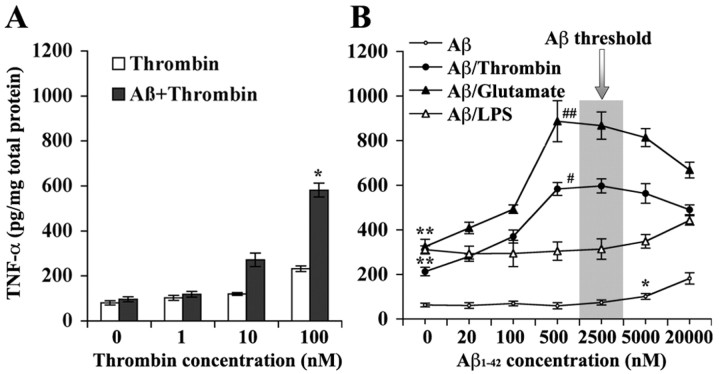
Figure 1.
Subthreshold soluble Aβ induced microglial hyper-reactivity to GPCR activators. A, Primary mouse brain microglial cultures were pretreated (5 min) with Aβ1-42 (500 nm), followed by increasing doses of thrombin (24 hr) as indicated (n = 4). *p < 0.01, Aβ pretreatment status versus thrombin dose by two-way ANOVA. B, N9 clonal murine microglial cells were exposed to increasing doses of Aβ1-42 as indicated for 24 hr or for 5 min, followed by a single dose of thrombin (100 nm), glutamate (2 mm), and LPS (5 ng/ml), respectively, for an additional 24 hr (n = 6). Compared with the untreated control, a single dose of thrombin (**p < 0.001), glutamate (**p < 0.001), or LPS (**p < 0.001) significantly stimulated TNF-α release. Aβ1-42 alone can directly induce TNF-α release dose dependently but with doses higher than 5 μm (threshold; *p < 0.05 compared with untreated control). Moreover, subthreshold Aβ1-42 pretreatment (without direct effect) dose dependently potentiated effects of thrombin (#p < 0.01, Aβ vs Aβ/thrombin by ANOVA) and glutamate (##p < 0.001, Aβ vs Aβ/glutamate by ANOVA) but not LPS (p > 0.05, Aβ vs Aβ/LPS by ANOVA) on TNF-α production in N9 microglial cells.