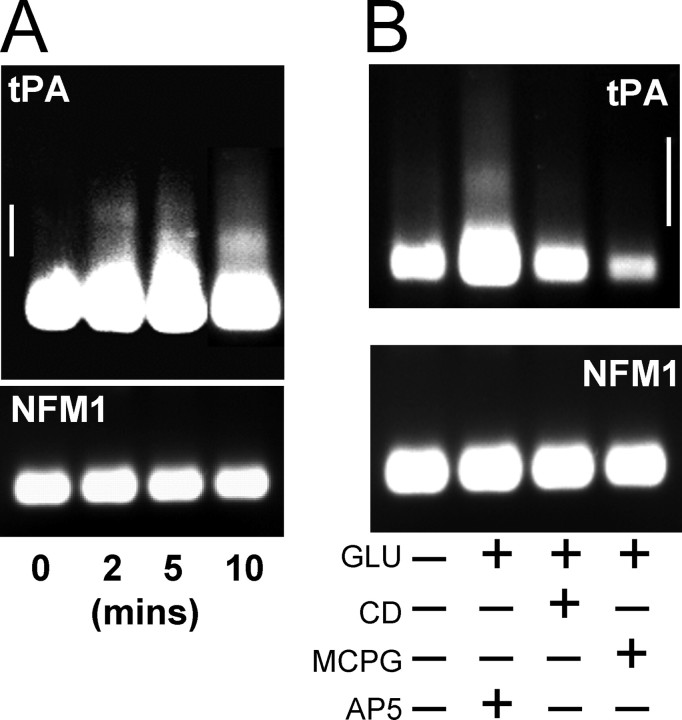
Figure 7.
tPA mRNA is rapidly polyadenylated after glutamate stimulation. A, Cultured hippocampal neurons (14-16 DIV) were stimulated with glutamate for 2, 5, and 10 min, and the poly(A)-tail length was determined by PAT assay. An increase in poly(A)-tail length was evident even at 2 min after glutamate stimulation. B, Inhibition of polyadenylation by cordycepin (CD) and MCPG. Cultured neurons as in A were treated with CD, MCPG, or AP-5 before and during glutamate stimulation. Poly(A)-tail length was determined 10 min after glutamate stimulation. CD and MCPG both inhibited the glutamate-induced polyadenylation of tPA mRNA. Neurofilament mRNA (NFM1) polyadenylation was not altered under any condition. Representative experiment shown; similar results were obtained in n = 3 experiments for both A and B. Scale bar shown on side of tPA gels represents 250 nucleotides.