Figure 1.
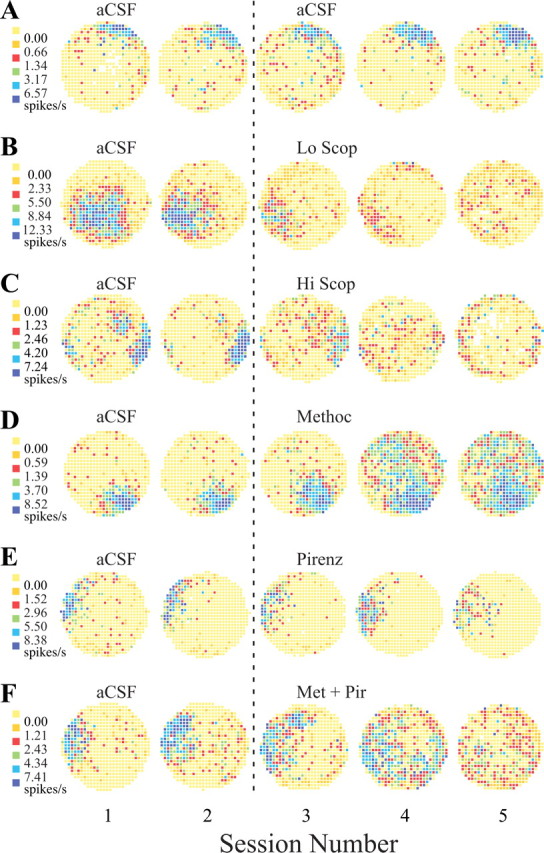
Example firing rate maps from place cells. In these maps, increasing firing rates are represented in color. Yellow represents pixels in which the firing rate was exactly zero over the entire 16 min session. To permit direct contrasts with other maps, the breakpoints between color categories (left end of each row) found for the first of each set are used for all five sessions in that row. A1, Rate map from the first control session. The firing field is against the wall at 1 o'clock. The very low density of nonzero pixels outside the field reflects the strong positional signal of this place cell. A2, The rate map for the second control session is very similar to the map from the first session, indicating that place-cell activity is strongly stationary in constant circumstances. A3-A5, In B-F, these sessions usually show the effects of dialyzing muscarinic antagonists. Here, however, the infusion of aCSF is maintained, providing a test for the stability of place-cell firing. The great similarity of each map in terms of the location of the firing field and the color coding required to represent the same breakpoints between categories indicates that this cell indeed showed constancy during the entire recording protocol. B, Dialysis of a low (0.5 mm) concentration of scopolamine. B1, In the first control (aCSF) session, this cell had a large firing field away from the cylinder wall at 7 o'clock. B2, The firing field in the second aCSF session is somewhat smaller than in the first session and is displaced slightly toward the cylinder wall. Nevertheless, the field is substantially the same in shape, size, position, and firing rate profile. B3, The first session during dialysis of 0.5 mm scopolamine. The field is now substantially smaller and considerably reduced in intensity, but its position is approximately the same as during the control recordings. B4, In the second drug session, the field weakens further but remains in about the same position. B5, In the final low-scopolamine session, the original field is gone. The cell now shows weak firing in other locations. C, Dialysis of high (2.0 or 3.0 mm) concentrations of scopolamine. C1, The firing field is against the wall at approximately 3:30 o'clock. There is a secondary patch of firing at ∼60% of the distance from the cylinder center at 1:30 o'clock. C2, The main field is constant during the second control session, whereas the secondary firing area is considerably weaker. C3, The main field is weakened during the first scopolamine session, and there is scattered firing over most of the cylinder surface. C4, A weak trace of the main field remains, and there is weak firing over the whole cylinder area. C5, Weak firing is mostly confined to the cylinder edge, in part because the rat tends to spend less time in the cylinder center. D, Dialysis of 1.0 mm methoctramine. D1, The firing field in the first control (aCSF) session is at 4:30 o'clock. D2, The firing field is essentially unchanged in the second aCSF session. D3, The field is hardly changed after the first session during dialysis of methoctramine. D4, During the second drug session, there is a very large, intense increase in out-of-field firing. D5, In the last methoctramine session, the out-of field firing persists. Increased out-of-field firing was characteristic of methoctramine administration, although the delayed onset and continued activity in the final session were atypical. E, Dialysis of 3.0 mm pirenzepine. D1-D4, The firing field at 9:30 o'clock is constant for the two aCSF sessions and the first two pirenzepine sessions. D5, In the final drug session, the firing field is considerably weaker than in the previous sessions, but it is still in the same position. F, Dialysis with 1.0 mm methoctramine plus 3.0 mm pirenzepine. F1, The firing field is at 9 o'clock in the first aCSF session. F2, The field is hardly different in the second aCSF session. F3, Although the field is substantially the same during the first session with the drug mixture, there appears to be some fragmentation with additional firing at 11:30 o'clock. F4, The positional firing pattern becomes quite fragmented, however, without much decrease in firing rate. F5, The original field is gone in the final drug session, leaving only sporadic firing that is quite spatially homogeneous. Scop, Scopolamine; Methoc, methoctramine; Pirenz, pirenzepine; Met + Pir, methoctramine plus pirenzepine.
