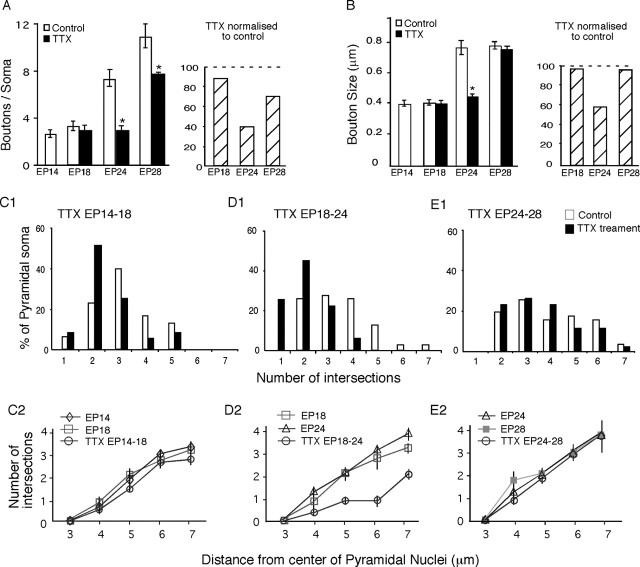
Figure 8.
Quantification of activity-dependent maturation of perisomatic innervation in cortical organotypic culture. A, TTX treatment between EP18 and EP24 and EP24 and EP28 prevents the increase of bouton density around pyramidal cell soma (Mann-Whitney U test; p < 0.001). Right, Effects of TTX treatment normalized to age-matched control. B, The increase of basket axon bouton size between EP18 and EP24 is prevented by TTX treatment (Mann-Whitney U test; p < 0.001). Right, Effects of TTX treatment normalized to age-matched control. C-E, Reverse Three-Dimension Sholl analysis of basket axon terminal complexity around pyramidal cell soma in TTX-treated slices compared with age-matched controls. C1-E1, Pyramidal cells are grouped according to the average number of intersections between a 7 μm Sholl sphere from the center of their nuclei and basket axon branches surrounding them. The developmental increase in the percentage of pyramidal cell somata surrounded by more complex basket axon terminal branches is blocked by TTX treatment between EP18 and EP24 (χ2 test; p < 0.001). However, TTX treatment between EP24 and EP28 has no effect (χ2 test; p = 0.9), suggesting that, once extended, basket terminal branches can be maintained around pyramidal cell soma despite reduced level of activity. C2-E2, An alternative method to quantify basket axon terminal complexity around pyramidal cell soma, by plotting of the number of intersections between basket axons and Sholl spheres with increasing radius from the center of a pyramidal nucleus. TTX treatment between EP18 and EP24 dramatically reduces the number of intersections and therefore the complexity of basket axon branches close to pyramidal cell soma.