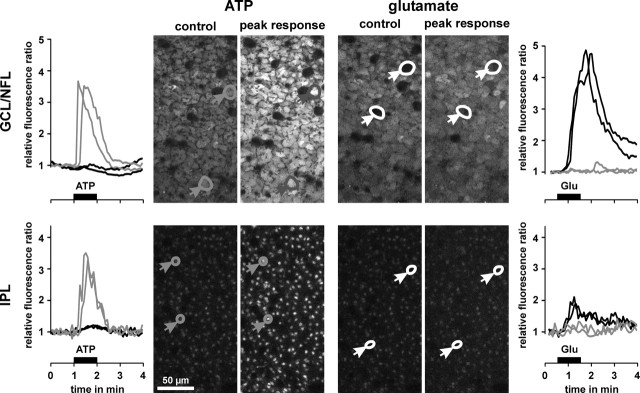
Figure 4.
Glutamate evokes intracellular calcium rises in retinal neurons but not in glial cells. Example of records in one whole mount of the guinea pig retina. Middle, Confocal views of the GCL-NFL (top) and IPL (bottom), respectively. The views were recorded before (control) and at the peak calcium responses after application of ATP (200 μm) and glutamate (1 mm), respectively. In the case of ATP application, glial cell end feet and profiles responded with transient calcium rises (left, gray traces), whereas neuronal cell bodies and synaptic structures were unresponsive (left, black traces). On application of glutamate, neuronal cell bodies and synaptic structures showed calcium responses (right, black traces), whereas glial cell end feet and profiles were unresponsive (right, gray traces).