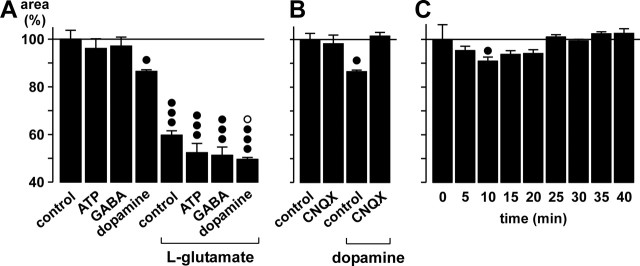
Figure 8.
Dopamine evokes morphological alterations via stimulation of endogenous glutamate release. The areas of the glial cell profiles in the IPL are given as percentage of control (100%). A, Effects of ATP (200 μm), GABA (1 mm), or dopamine (100 μm) at control conditions and during co-exposure with glutamate (1 mm). B, The AMPA-kainate receptor blocker CNQX (50 μm) inhibits the dopamine effect on glial cell morphology. C, Time dependence of the dopamine (100 μm) effect. In A and B, the effects were measured after a 10 min exposure. Means ± SEM of 3-10 experiments. Significant differences versus control: •p < 0.05; •••p < 0.001. Significant effect of dopamine during glutamate exposure: ○p < 0.05.