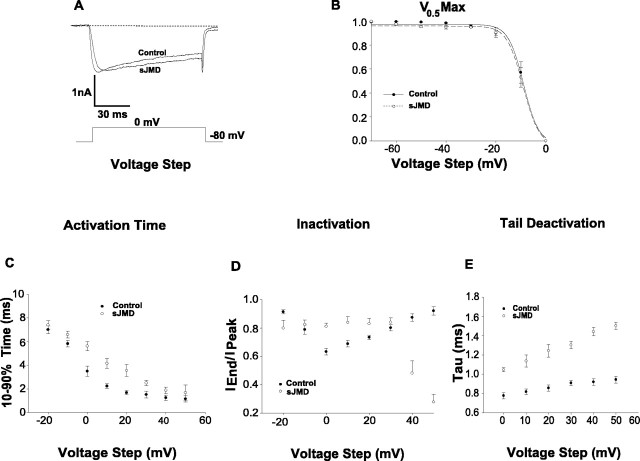
Figure 2.
Effects of sJMD on the voltage gating and kinetics of HVA Ca2+ current. A, Superimposed control and normalized sJMD calcium current traces. Note that current suppression occurs with a delay in activation time, a slowing of inactivation, and an increase in tail deactivation time. B, Raw data fitted to a Boltzmann function. Note that the sJMD does not change the voltage dependence of the ion channel steady-state inactivation. C, Ten to 90% activation time as a function of voltage step. Note that the sJMD delays voltage-dependent current activation. D, Iend/Ipeak inactivation index as a function of voltage step. Note that the sJMD decreases Ca2+-dependent inactivation at intermediate voltage while promoting a closed-state ion channel at both lower- and upper-end voltage values. E, Tau tail deactivation parameter as a function of voltage step. Note that the sJMD prolongs Ca2+channel closure as indicated by an increase in deactivation time (control, n = 10; sJMD, n = 9). Values are expressed as mean ± SE.