Figure 2.
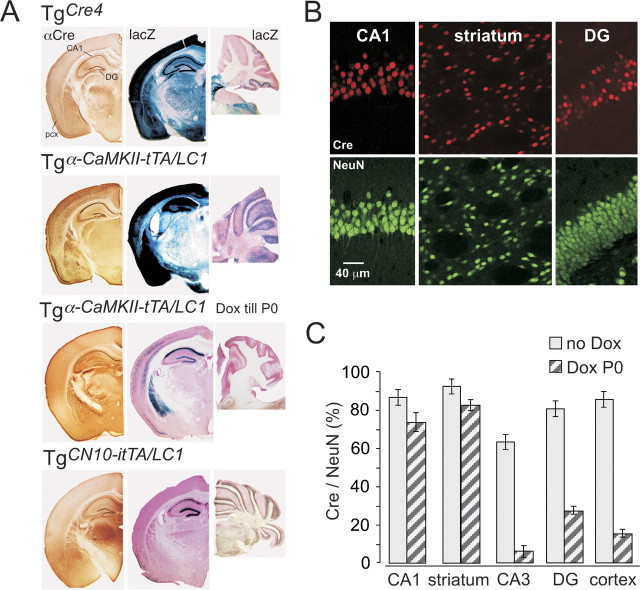
Regulation of Cre expression in mouse forebrain. A, Cre-immunolabeled (αCre) and corresponding X-gal-stained (lacZ) coronal brain sections and sagittal X-gal-stained cerebellar sections of TgCre4, Dox-naive (no Dox), and prenatally Dox-treated (Dox till P0) Tgα-CaMKII-tTA/LCR and TgCN10-itTA/LC1 mice. All sections were taken between P30 and P60 from mice that carried the Cre-indicator lacZ gene Rosa+/R26R to permit the visualization of Cre activity by X-gal staining. CA1, CA1 stratum pyramidale; pcx, piriform cortex. B, Confocal analysis of Cre- and NeuN-immunolabeled neurons in hippocampal CA1, DG neurons, and striatum in prenatally Dox-treated Tgα-CaMKII-tTA/LC1/Rosa+/R26R mice at P30. C, Ratios of Cre-positive to NeuN-positive neurons, in several brain regions (CA1 and CA3 stratum pyramidale, dentate gyrus, striatum, and somatosensory cortex layer 5/6). Ratios (error bars, mean ± SD) were assessed by confocal analysis (see B) from four sections of three Dox-naive and three prenatally Dox-treated mice. Note that prenatal Dox exposure increases the extent of mosaic expression substantially in some regions.