Figure 4.
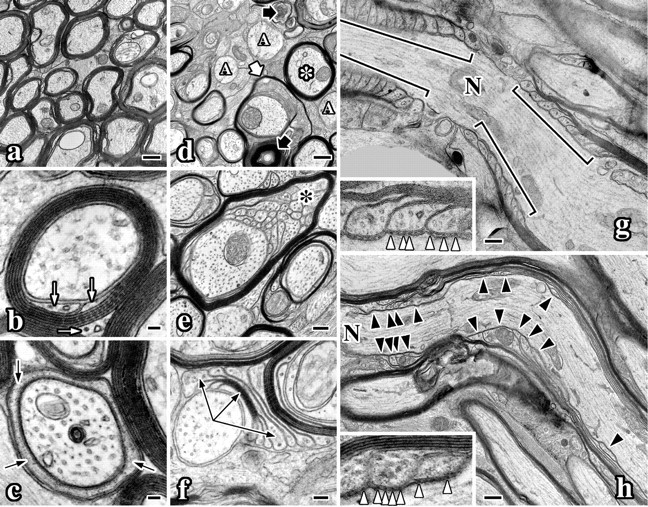
CNS myelin ultrastructural abnormalities in Nkx6-2 null mice. Electron micrographs of optic nerves from 7-month-old wild-type (a-c, g) and Nkx6-2 null (d-f, h) mice. a, Transverse section of wild-type optic nerve. b, Wild-type myelinated axon sectioned through the internode. The inner tongue process is visible (white arrows). c, Wild-type myelinated axon sectioned through the paranode. Cytoplasm in a paranodal loop is visible (black arrows). d, Transverse section of mutant optic nerve shows redundant loops (thick white arrow), thin myelin (asterisk), unmyelinated axons (“A”), and axonal degeneration (thick black arrows). e, Stable vermicular-like processes (black asterisk) underneath a myelin sheath in mutant optic nerve. f, Compact myelin flap flanked by paranodal loops (arrows) in optic nerve from null mice. g, Longitudinal section of a wild-type node of Ranvier (N). h, Longitudinal section of a node of Ranvier from a null mouse. Paranodal loops are disorganized (black arrowheads). g, h, Insets show axoglial junctions (white arrowheads). Scale bars: a, d, g, h, 500 nm; b, c, 50 nm; e, 200 nm; f, 100 nm; insets, g, h, 150 nm.
