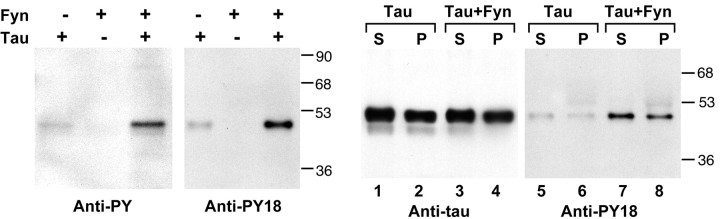
Figure 3.
Left, In vitro tyrosine phosphorylation of tau by fyn. In vitro kinase reactions were performed with E. coli-synthesized tau and fyn as described in Materials and Methods. Reactions were probed with either anti-phosphotyrosine (4G10, left panel) or anti-PY18 (right panel). Note that fyn kinased tyr18 in vitro as evidenced by the acquisition of anti-PY18 and anti-PY reactivity after incubation of tau with fyn. Right, Microtubule binding activity of tyrosine-phosphorylated tau. E. coli-synthesized tau, incubated with or without kinase, was incubated with taxol-stabilized microtubules, as described in Materials and Methods. The supernatants containing unbound tau (S, odd lanes) and the pellets containing microtubule bound tau (P, even lanes) were examined for the presence of tau. Tau in lanes 1, 2, 5, and 6 was from a control kinase reaction without fyn, whereas tau in lanes 3, 4, 7, and 8 was from a fyn kinase reaction. The left panel was probed for total tau. The right panel was probed with anti-PY18. Note that the distribution of tyrosine-phosphorylated tau between the supernatant and pellet was similar to that of nonphosphorylated tau.