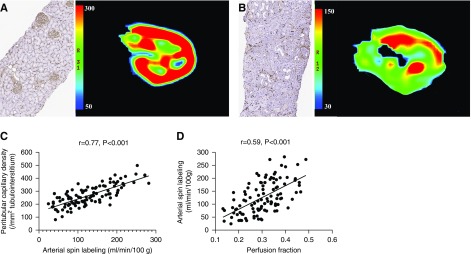
Figure 2.
Assessment of allograft peritubular capillary density with functional MRI-based perfusion quantification. (A and B) Compared with normal allografts (A) with well preserved peritubular capillaries, allografts with severe interstitial fibrosis (B) had peritubular capillary rarefaction and significantly lower allograft perfusion, as suggested by the reduced peritubular capillary density (CD34) and lower arterial spin labeling readings, respectively, in (B) than in (A) (Original magnification, ×40). (C) Allograft arterial spin labeling readings were significantly correlated with peritubular capillary density in the allograft injury group (r=0.77; P<0.001). (D) Arterial spin labeling readings were significantly correlated with cortical perfusion fraction calculated from diffusion-weighted imaging (r=0.59; P<0.001).