FIGURE 1.
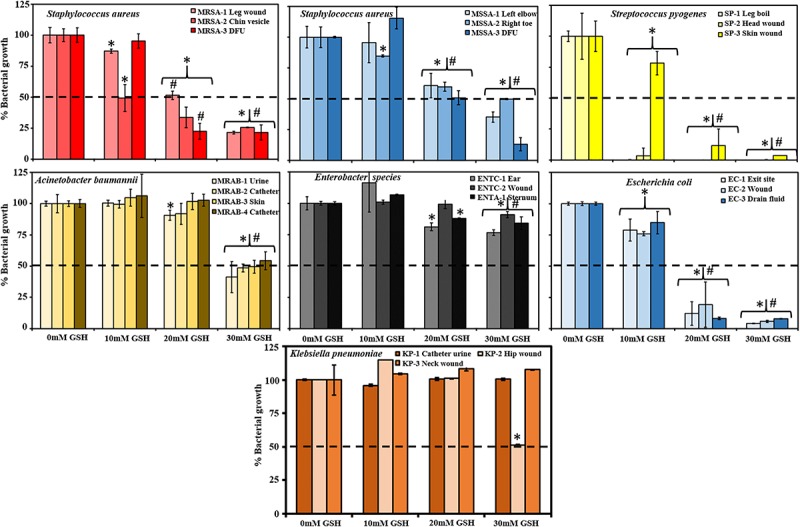
Effect of Glutathione (GSH) on growth of bacterial species isolated from Sydney hospitals. GSH showed concentration-dependent effects in inhibiting bacterial growth. 10 mM GSH did not affect bacterial growth for most of the isolates whereas; 20 mM GSH showed around 50% decrease in bacterial growth for all isolates of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Methicillin-sensitive S. aureus (MSSA) and a less then 25% decrease for one S. pyogenes and E. coli. 30 mM GSH is very effective inhibiting greater than 50% growth with almost complete inhibition in case of S. pyogenes and E. coli and resistance in case of Enterobacter species and K. pneumoniae. Data represent mean ± SD; n = 4 experiments performed in biological replicates. Dotted line (- - -) in each graph indicates 50% bacterial growth. ∗P < 0.05 (statistically significant) when compared to control, #P < 0.05 (statistically significant) when compared to 10 mM GSH.
