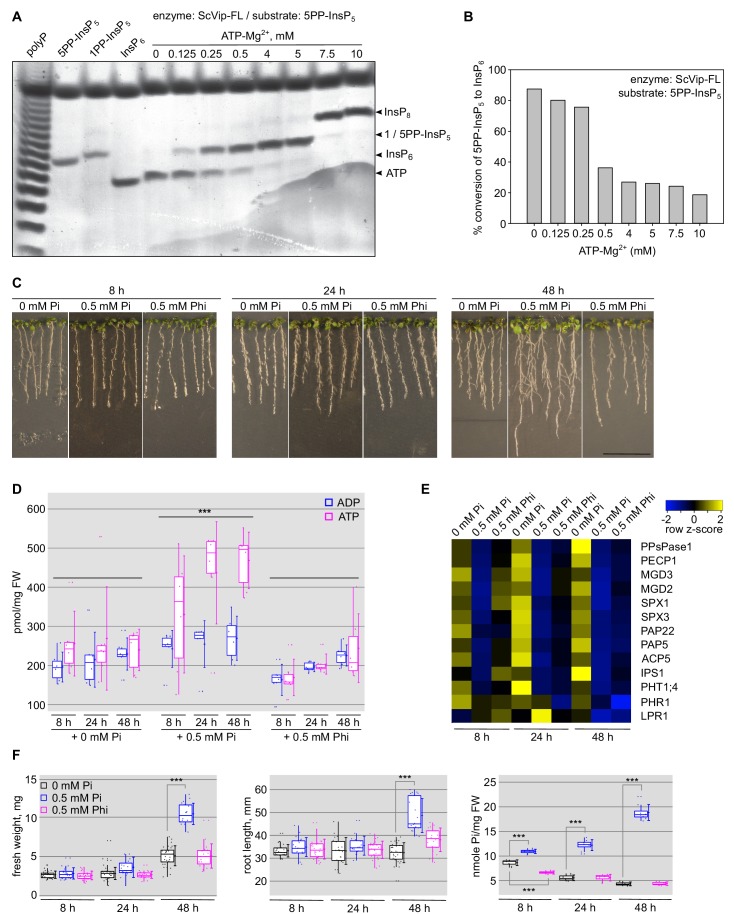
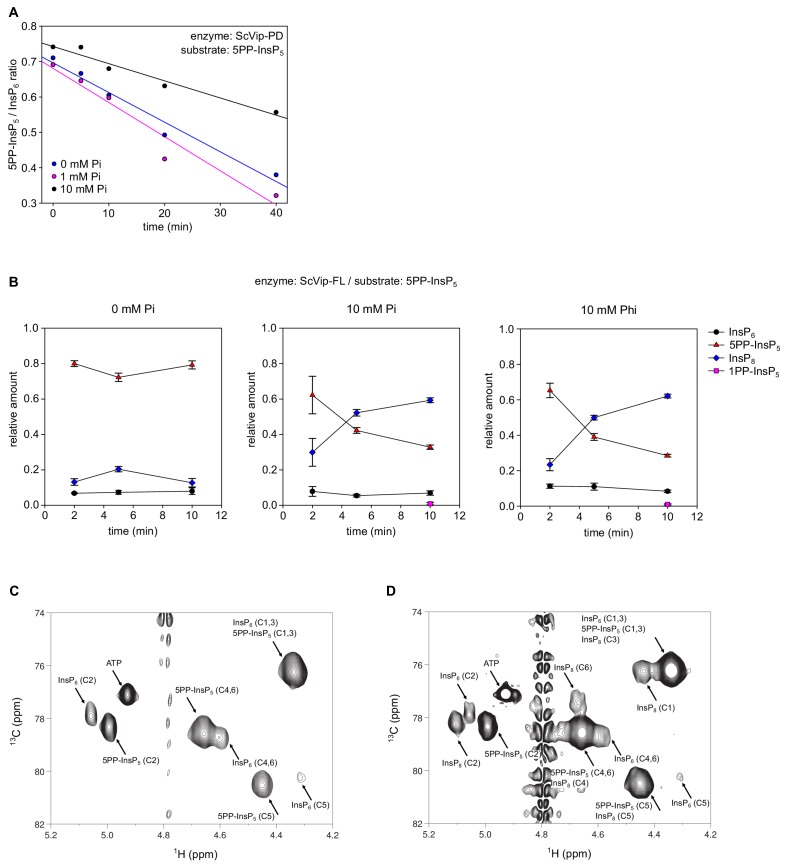
Figure 6. Changes in cellular ATP levels affect the relative PPIP5K kinase and phosphatase activities.
(A) Bi-functional PP-InsP activity assay of ScVip1. Reactions containing 2 μM protein, 40 μM 5PP-InsP5 and various ATP-Mg2+ concentrations were incubated at 37°C for 45 min. Product PP-InsPs were separated on a native PAGE gel and stained with toluidine blue. The bands corresponding to InsP6, 1/5PP-InsP5, InsP8 and ATP are indicated by arrow heads. (B) Quantification of conversion of the 5-PP-InsP5 (substrate) to InsP6 (product) by full-length ScVip1 (FL) enzyme in reactions containing different concentrations of ATP-Mg2+, recorded by NMR specroscopy. (C) Col-0 seedlings 6 DAG were transplanted from 1/2MS plates to Pi-deficient 1/2MS plates and incubate 3 days more. Then, the seedlings were transplanted again to Pi-deficient 1/2MS plates supplemented with 0 mM Pi, 0.5 mM Pi or 0.5 mM Phi, and grown for additional 8 hr, 24 hr or 48 hr. (D) Determination of the cellular ATP and ADP concentrations of the seedlings shown in (C). (E) qRT-PCR quantification of PSI marker genes in the seedlings shown in (C). Expression levels are represented as Z-scores. The original qRT-PCR data are shown in Supplementary file 3e. (F) Quantification of seedling fresh weight, primary root length and cellular Pi concentrations of the plants shown in (C).