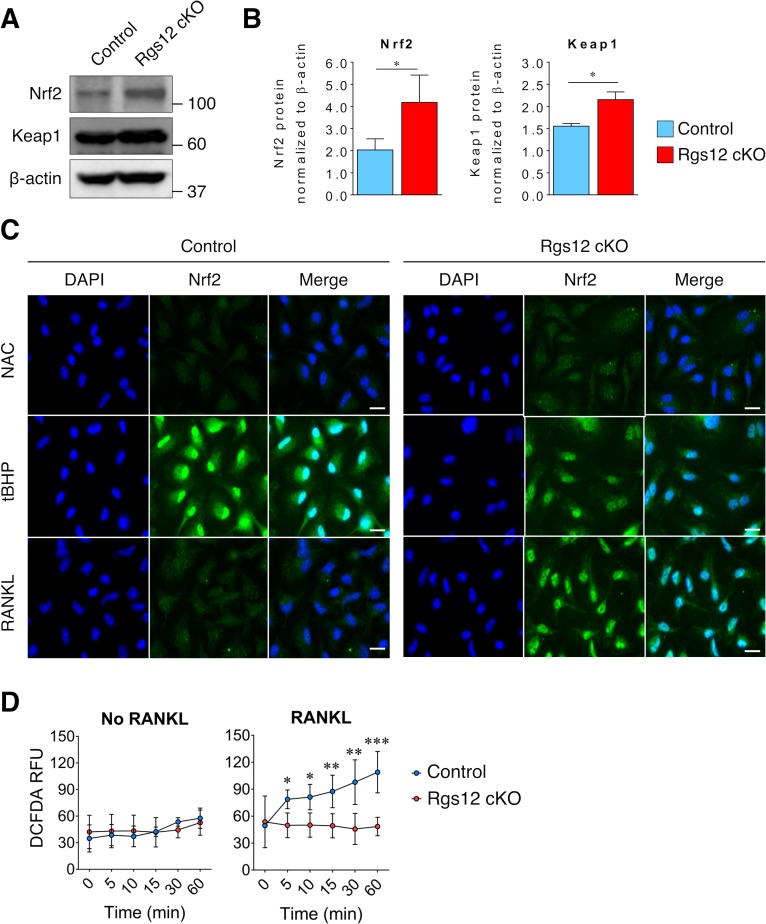
Figure 4. Increased Nrf2 activation and expression of antioxidant proteins in Rgs12-deficient osteoclast precursors.
(A–B) Immunoblot of Nrf2 and Keap1 protein levels in Rgs12 cKO and control BMMs treated with RANKL for 72 hr. Densitometry analysis was performed on bands and normalized to β-actin (N = 3, *p<0.05). (C) Nrf2 immunofluorescence staining in Rgs12 cKO and control BMMs differentiated with M-CSF and RANKL for 72 hr. As a negative control for Nrf2 nuclear translocation, cells were treated with the antioxidant compound NAC (5 mM, 16 hr) to suppress cellular ROS. Conversely, as a positive control for Nrf2 nuclear translocation, cells were treated with the peroxidase tBHP (50 μM, 16 hr) to induce oxidative stress. (D) Induction of ROS levels in Rgs12 cKO and control BMMs differentiated for 72 hr, kept in serum-free medium for 6 hr, and stimulated with RANKL for the indicated times. ROS levels were measured using the DCFDA fluorescence method. Data are means ± SD (N = 5, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). DAPI, 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; NAC, N acetylcysteine; tBHP, tert-butylhydroxyperoxide. ROS, reactive oxygen species. DCFDA, 2’,7’-dichlorofluorescin diacetate. RFU, relative fluorescence units..