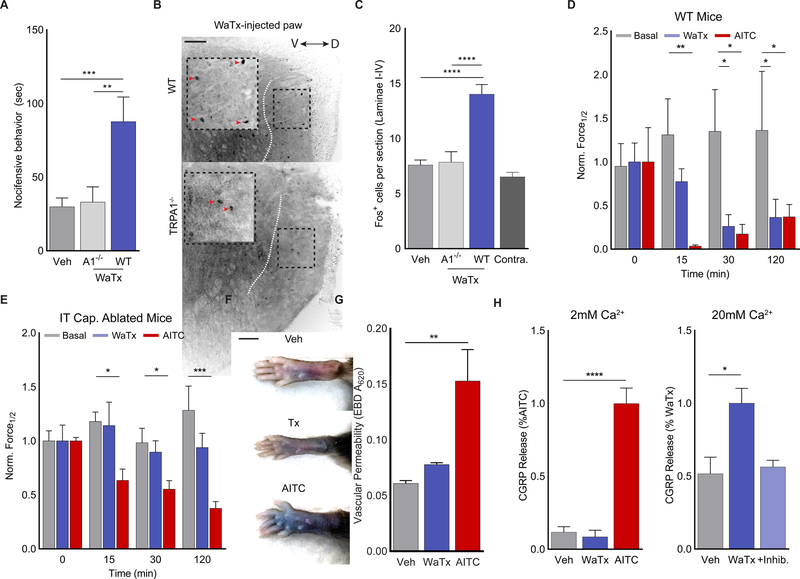
Figure 5. WaTx elicits TRPA1-dependent non-inflammatory pain.
(A) WaTx-evoked nocifensive behavior in mice. One-way ANOVA with post-hoc Holm-Sidak correction for multiple comparisons; n = 12–20 mice/group.
(B, C) Induction of cFOS expression in the superficial laminae of the mouse spinal cord (dorsal to the dotted white line) after WaTx injection. Orientation of spinal cord along the dorsoventral axis indicated with bidirectional arrow. Inverted grayscale image with scale bar = 100 μm. One-way ANOVA with post-hoc Holm-Sidak correction for multiple comparisons; n = 22–39 sections/group.
(D, E) Timecourse and magnitude of mechanical allodynia onset in (D) wild-type (n = 8 animals/treatment) and (E) intrathecally capsaicin ablated mice (n = 6–8 mice/treatment) in response to vehicle, WaTx (100nM), or AITC injection (0.75% v/v in mineral oil). One-way ANOVA with post-hoc Holm-Sidak correction for multiple comparisons.
(F) Paw edema and (G) vascular permeability in mice after WaTx (100nM) or AITC (0.75% v/v in mineral oil) injection. One-way ANOVA with post-hoc Holm-Sidak correction for multiple comparisons; n = 4 mice/treatment. Scale bar: 5 mm.
(H) Measurements of CGRP release cultured neonatal rat trigeminal neurons under physiological (2mM) and high (20mM) extracellular Ca2+ conditions. Treatments: vehicle (PBS, pH 7.4), WaTx (10 μM), AITC (100 μM), and inhibitor A 967079 (10μM). One-Way ANOVA with post-hoc Holm-Sidak correction for multiple comparisons; n = 6–12 treatments/condition.
All summary data, mean ± SEM. See also Figure S5.