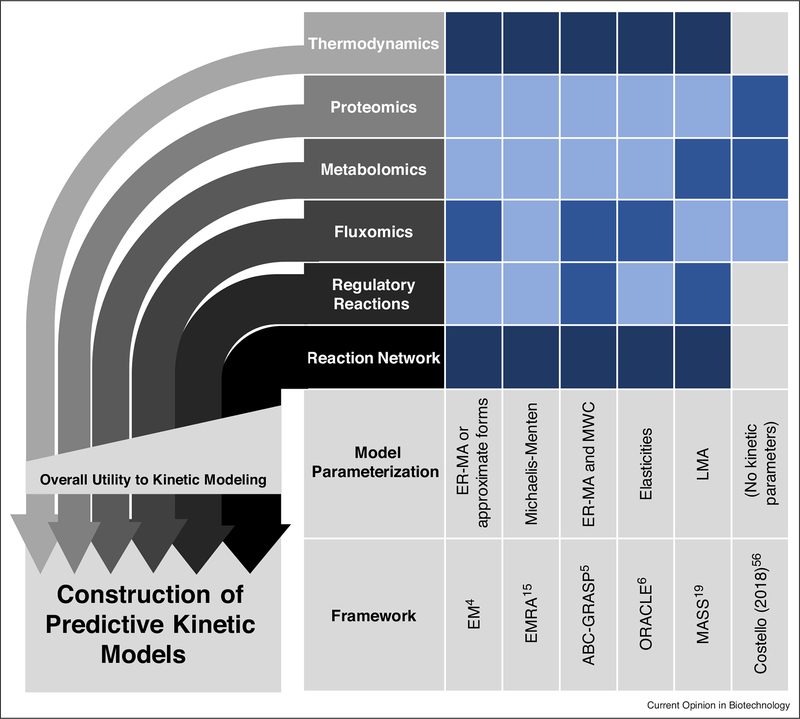
Figure 1.
Different data types have varying value to kinetic modeling frameworks.
-omics types are required to varying levels by different model frameworks (darkest boxes indicate data type is required, less dark boxes indicate data type is used to a high degree in practice, lighter blue boxes indicate data type can be used, light gray boxes indicate data type is not used) [4,5,6,15,19,57••]. While all the -omics data types shown have utility in kinetic modeling, modeling results are usually most sensitive to variation in those near the bottom (e.g. variation in network structure). Thus, those data types generally provide more utility to kinetic modeling efforts and should be prioritized. Note that while regulatory reactions provide much value to kinetic modeling, they are not always incorporated, either because they are unknown or because they cannot be incorporated easily using a given framework. Data-driven models, while requiring very large amounts of data, may not require knowledge of the reaction network or regulatory interactions at all [57••].
ABC-GRASP, Approximate Bayesian Computation – General Reaction Assembly and Sampling Platform; EM, Ensemble Modeling; EMRA, Ensemble Modeling for Robustness Analysis; ER-MA, Elementary Reaction Mass Action; LMA, Law of Mass Action; MASS, Mass Action Stoichiometric Simulation; MWC, Monod-Wyman-Changeux; ORACLE, Optimization and Risk Analysis of Complex Living Entities.