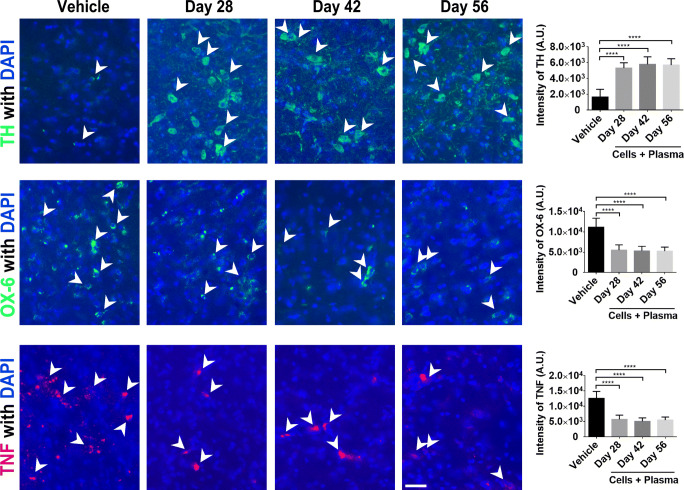
Fig. 5.
Administration of cord blood cells with plasma in the 6-OHDA PD rat model: Assessment of TH-positive dopaminergic neurons, immune cell activation, and pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) staining (top row) was used to investigate the potential effect of combined cord blood cell with plasma injection on dopaminergic neuron populations in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc). Analysis of fluorescent intensity revealed significant protection and retention of dopaminergic cells in the SNpc in 6-OHDA animals treated with cord blood cells and plasma, compared to vehicle controls. Cord blood treated groups also demonstrated significant reductions immune cell activation (OX-6) and pro-inflammatory cytokine production (TNF). Overall, the combination of cord blood cells and plasma can significantly modulate the exacerbated immune response through downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokine production and immune cell activation in the 6-OHDA rat model at all time points tested. Photomicrographs correspond to representative SN in coronal sections immune-labeled with TH, OX-6 or TNF antibody. Scale bar = 50 μm