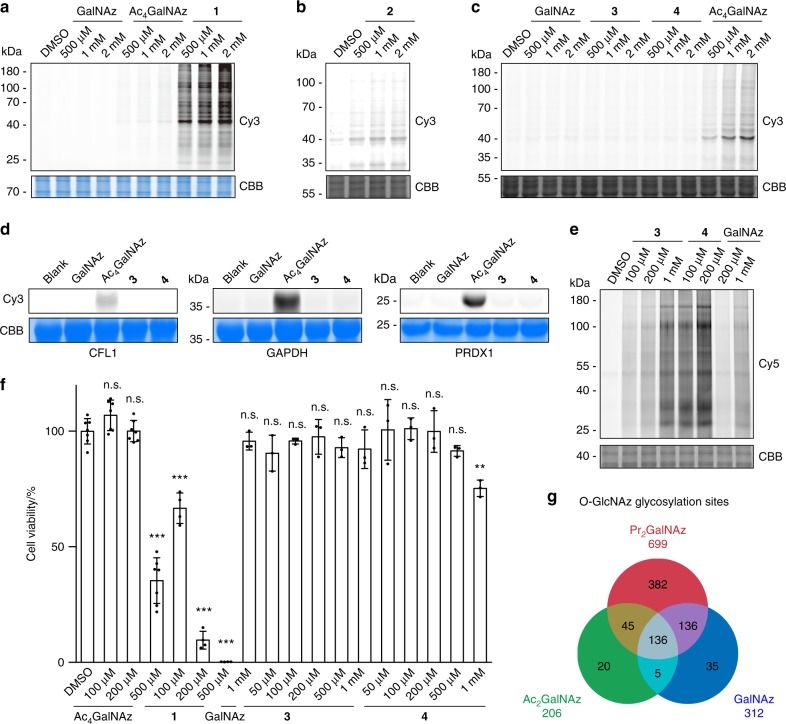
Fig. 2.
Labeling efficiency and specificity of 1,3-Ac2GalNAz and 1,3-Pr2GalNAz. a–c In-gel fluorescence scanning showing HeLa cell lysates treated with respective unnatural monosaccharides at varied concentrations for 2 h, followed by reaction with alkyne-Cy3. d In-gel fluorescence scanning showing purified CFL1, GAPDH, and PRDX1 treated with 1 mM of respective unnatural monosaccharides for 2 h, followed by reaction with alkyne-Cy3. e In-gel fluorescence scanning showing HeLa cells incubated with respective unnatural monosaccharides at varied concentrations for 48 h, followed by reaction with alkyne-Cy5. Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB)-stained gels in a–e demonstrate equal loading. In a–e representative results are from three independent experiments. f Cell counting assay by CCK-8 kit showing viability of HeLa cells incubated with respective unnatural monosaccharides at varied concentrations for 48 h. Error bars represent mean ± s.d. Results are from at least three independent experiments (for DMSO and Ac4GalNAz, n = 7; for 1, n = 4; for GalNAz, 3 and 4, n = 3). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, n.s., not significant (one-way ANOVA). g Overlap of O-GlcNAz sites identified in HeLa cells treated with GalNAz (based on the data set from ref. 8), 1,3-Ac2GalNAz and 1,3-Pr2GalNAz. Source data for figures a–f are provided as a Source Data file