Fig. 4.
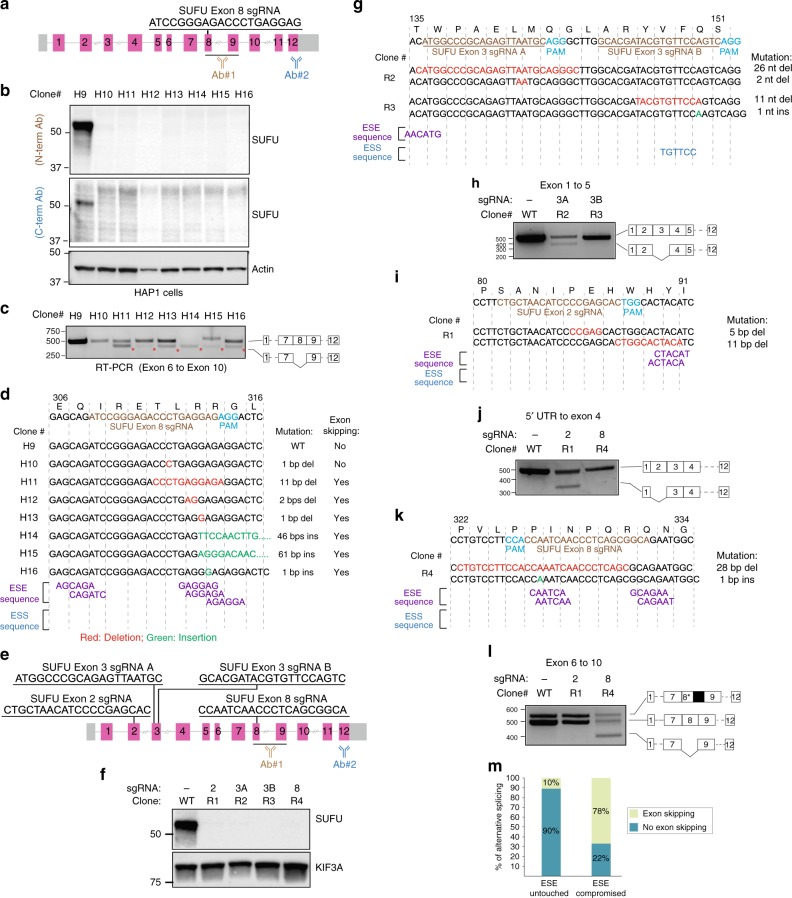
Compromised ESEs account for INDEL-induced exon skipping. a Genomic structure of SUFU and exonic sequence targeted by SUFU exon 8 sgRNA. The recognition sites of antibodies used in panel b are indicated. b Western blot analysis of HAP1 cells edited with SUFU exon 8 sgRNA shows no detectable expression of SUFU. c Exon skipping is prevalent in CRISPR-Cas9-edited SUFU clones. RT-PCR analysis using primers flanking exons 6 and 10 of SUFU in CRISPR-Cas9-edited SUFU clones. Sequencing of amplicons reveals exon skipping in all of clones except clones H9 and H10. d Disruption of exon splicing enhancers (ESEs) by CRISPR-introduced INDELs triggers skipping of the edited exons. Genetic mutation and the presence/absence of exon skipping events for each clone are indicated. Putative ESEs were identified using the RESCUE-ESE web server. e Multiple sgRNA sequences located in symmetric or asymmetric exons of the SUFU gene used for targeted disruption of ESEs. f sgRNAs described in “e” were used to edit the SUFU gene in RMS13 cells. Western blot analysis of lysates derived from the CRISPR-Cas9-edited RMS13 clones show no detectable SUFU protein. g Genomic sequences of RMS13 clones edited with SUFU exon 3 sgRNAs. CRISPR-introduced mutations and putative exon splicing enhancer (ESE) and exon splicing silencer (ESS) sequences are indicated. h RT-PCR analysis and cDNA sequencing result of clones R2 and R3 using primers flanking exon 1 and 5. i Genomic sequences of RMS13 clones edited with SUFU exon 2 sgRNA. CRISPR-introduced mutations and putative ESE/ESS sequences are indicated. j RT-PCR analysis and cDNA sequencing result of clones R1 and R4 using primers flanking 5′ UTR and exon 4. k Genomic sequences of RMS13 clones edited with SUFU exon 8 sgRNA. CRISPR-introduced mutations and putative ESE and ESS sequences are indicated. l RT-PCR analysis and cDNA sequencing result of the clones R1 and R4 using primers flanking exon 6 and exon 10. m Disruption of ESE code is highly reliable in anticipating CRISPR-Cas9-induced exon skipping. Twenty-four CRISPR-Cas9-edited cell lines with different mutations were analyzed for the presence/absence of exon skipping events and changes in ESE sequences due to CRISPR-introduced INDELs. Source data are provided as a Source Data file