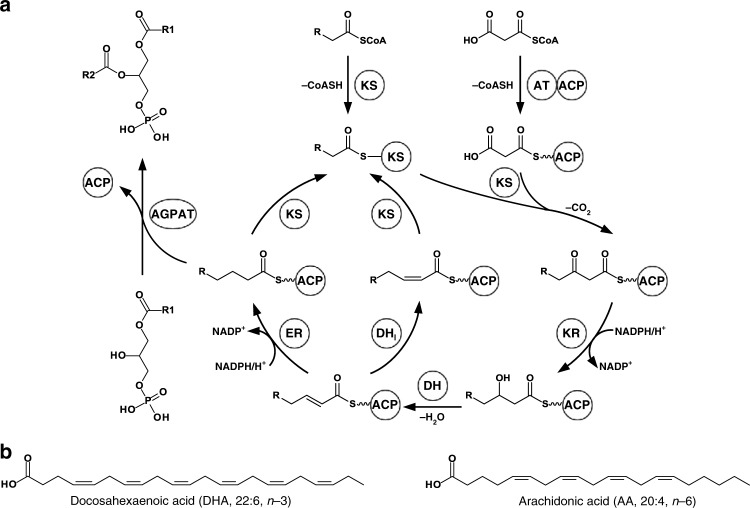
Fig. 1.
De novo polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) biosynthesis in myxobacteria by iteratively acting, multifunctional PUFA synthases. a The starter unit acetyl-CoA (R = H) is consecutively elongated with the extender unit malonyl-CoA by several rounds of decarboxylative Claisen condensations, resulting in the extension of the fatty acyl chain by two carbons per cycle. After each round of elongation, the β-keto group is either fully reduced by ketoreduction, dehydration plus enoylreduction, or only reduced by ketoreduction and dehydration, giving rise to the trans double bond, which is then isomerized to synthesize an acyl chain bearing methylene-interrupted cis double bonds. After reaching its final length, the fatty acyl chain is presumably used for acylation of the 2-position of 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate. KS, ketosynthase of Pfa2 and Pfa3; AT, acyltransferase of Pfa2 and Pfa3; ACP, acyl carrier protein of Pfa2; KR, ketoreductase of Pfa2; DH, dehydratase of Pfa2 and Pfa3; DHI, dehydratase/isomerase of Pfa3; ER, enoylreductase of Pfa1; AGPAT, 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase of Pfa3. b Structures of the main PUFAs produced by the myxobacteria Aetherobacter fasciculatus (SBSr002) and Minicystis rosea (SBNa008)