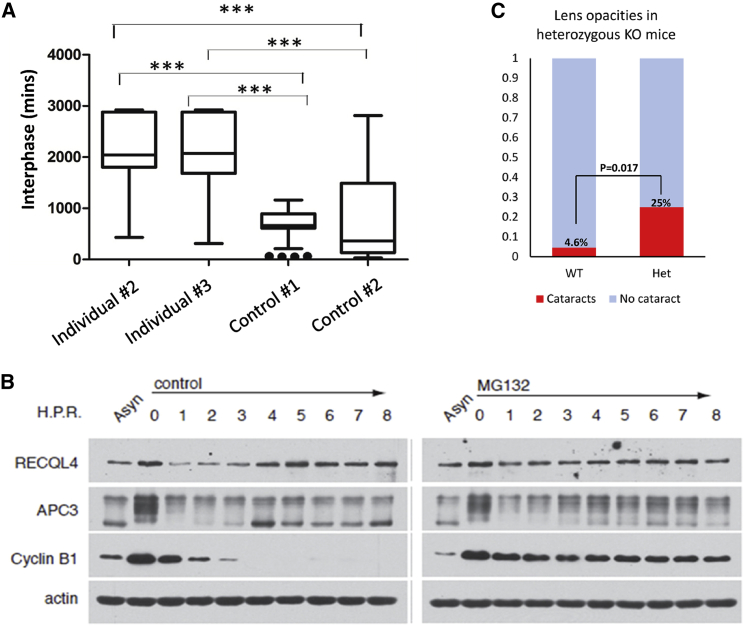
Figure 3.
Effect of ANAPC1 Deficiency and Cell Cycle Variations of RECQL4
(A) Fibroblasts derived from individuals homozygous for the ANAPC1 intronic variant spent a longer time at the interphase of the cell cycle compared to control fibroblasts (∗∗∗ = p < 0.001); the time-lapse microscopy was performed as described previously.26 The middle line represents the median, the box represents quartiles, and the whiskers represent minimum and maximum values within 1.5 times the interquartile range.
(B) Proteins from thymidine-nocodazole-synchronized-MG132-treated and non-treated HeLa cells at specific time points (0 to 8 hours) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblot. The upward-shifted (phospho) APC3 represents a marker for mitosis. The cyclin B disappearance represents a positive control for APC/C activity, and actin is used as a loading control. RECQL4 protein levels decreased within the first 3 h of mitosis and became stable after treatment with MG132, similar to classical APC/C substrates such as cyclin B. Asyn signifies asynchronous cells.
(C) Mice heterozygous for a loss-of-function Anapc1 mutation develop cataracts more frequently than wild-type mice (detailed data: no lens opacity in 2,766 WT (wild-type) mice and 12 het (heterozygous KO) mice, lens opacity in one eye in 116 WT mice and 4 het mice, lens opacities in both eyes in 17 WT mice and no het mice).