Figure 2.
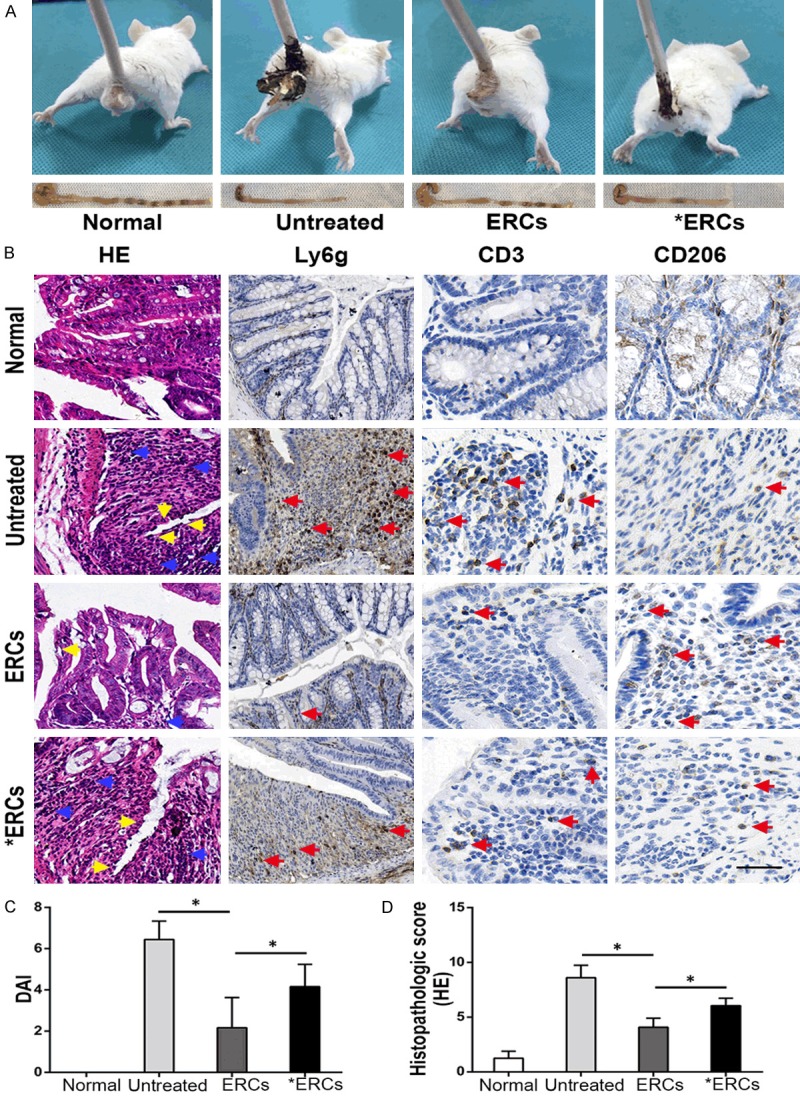
A. In vivo, the representative photos of mice with general performance were shown from different groups. B. Microscopic observation of the colon from different groups. In the untreated group, it was characterized by damaged epithelium (yellow arrow) and massive inflammatory cells infiltration (blue arrow) into the mucosa and submucosa. In ERCs-treated group, the colon showed improved epithelial and crypt structures (yellow arrow) and remarkably reduced infiltration of inflammatory cells (blue arrow). ERCs suppress intra-colon Ly6g+ cells and CD3+ T cells (pro-inflammatory) infiltration (red arrow) and promote CD206+ cells (anti-inflammatory) infiltration (red arrow) in the colitis mice. However, the blockage of ERCs with anti-PD-L1 mAb significantly impaired the therapeutic efficacy. C. The comparison of DAI was analyzed in different groups on day 15 (n=8 per group). Bar=100 μm. D. The comparison of the histopathological scores was performed in different groups on day 15 (n=8 per group). ERCs indicated ERCs treatment. *ERCs indicated anti-PD-L1 antibody pretreated ERCs treatment. *P<0.05.
