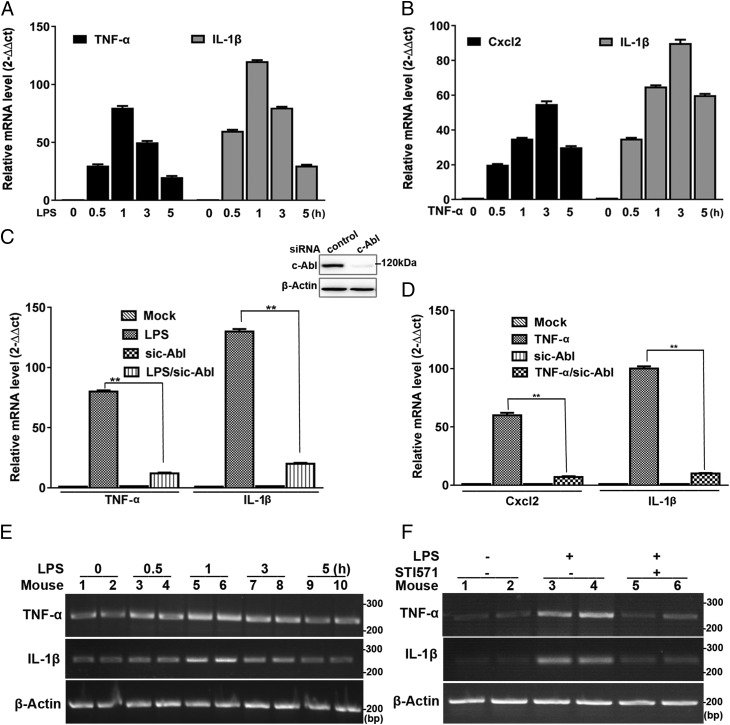
FIGURE 7.
Inflammatory agent-induced proinflammatory gene expression is enhanced by c-Abl. (A and B) Inflammatory agents stimulate inflammatory gene expression in murine macrophages. RAW 264.7 cells were incubated with LPS for various lengths of time. Real-time PCR was performed to detect the mRNA expression of TNF-α and IL-1β (n = 5) (A). RAW 264.7 cells were incubated with TNF-α for various lengths of time. Real-time PCR was performed to detect the mRNA expression of Cxcl2 and IL-1β (n = 5) (B). (C and D) c-Abl knockdown blocks upregulation of inflammatory genes. RAW 264.7 cells were subjected to siRNA targeting c-Abl and then mock treated or exposed to LPS for 1 h; real-time PCR was performed to detect the mRNA expression of TNF-α and IL-1β. Inset, Western blotting shows efficacy of c-Abl knockdown (n = 5) (C); c-Abl–deficient RAW 264.7 cells were mock treated or exposed to TNF-α for 3 h, and real-time PCR was performed to detect the mRNA expression of Cxcl2 and IL-1β (n = 5) (D), **p < 0.01. (E) LPS stimulates inflammatory gene expression in mice lungs. Mice were exposed to LPS through the intranasal route for various lengths of time. Mice lungs were collected, and homogenates were prepared. RNA was extracted, and RT-PCR was performed to detect mRNA expression of TNF-α and IL-1β (n = 5). Data were expressed as mean ± SD. Difference significance was analyzed by one-way ANOVA. (F) c-Abl inhibition blocks upregulation of inflammatory genes in mice lungs. Mice were exposed to LPS through the intranasal route for 1 h with or without an i.p. pretreatment of STI571. Mice lungs were collected, and homogenates were prepared. RNA was extracted, and RT-PCR was performed to detect the mRNA expression of TNF-α and IL-1β. Similar results were obtained from at least three independent experiments.