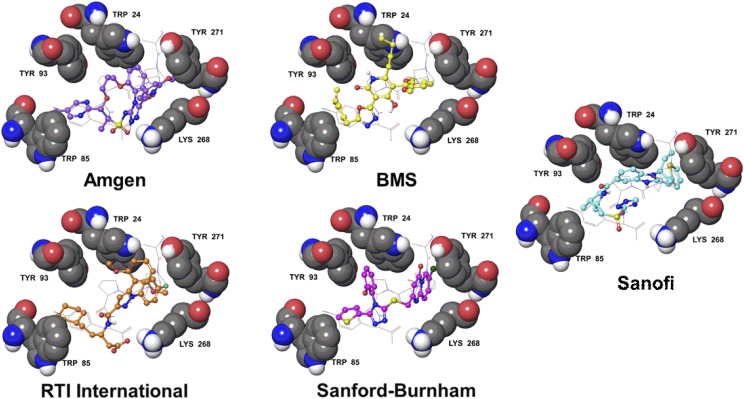
Fig. 8.
The apelin receptor structure from PDBID 5VBL (Ma et al., 2017) with docked poses of five series of apelin agonists. The apelin receptor residues, W24, W85, Y93, K268, and Y271 are labeled and displayed as gray space filling. The structure of the four C-terminal residues of the apelin analog from PDBID 5VBL are displayed as gray sticks. The receptor and peptide are overlaid with docked poses of an Amgen (violet balls and sticks), a Bristol-Myers Squibb (yellow balls and sticks), an RTI International (orange balls and sticks), a Sanford-Burnham (magenta balls and sticks), and a Sanofi (cyan balls and sticks) small molecule apelin agonist. Only polar hydrogens are shown. Structures were derived from the following patents: Amgen (Chen et al., 2017), Bristol-Myers Squibb (Myers et al., 2017), RTI International (Narayanan et al., 2016), Sanford-Burnham (Pinkerton and Smith, 2015), and Sanofi (Hachtel et al., 2014). Pinkerton and Smith (2015) confirmed the Sanford-Burnham apelin compounds were selective vs. the angiotensin II receptor (AT1), the most closely related GPCR, with no significant off target binding.